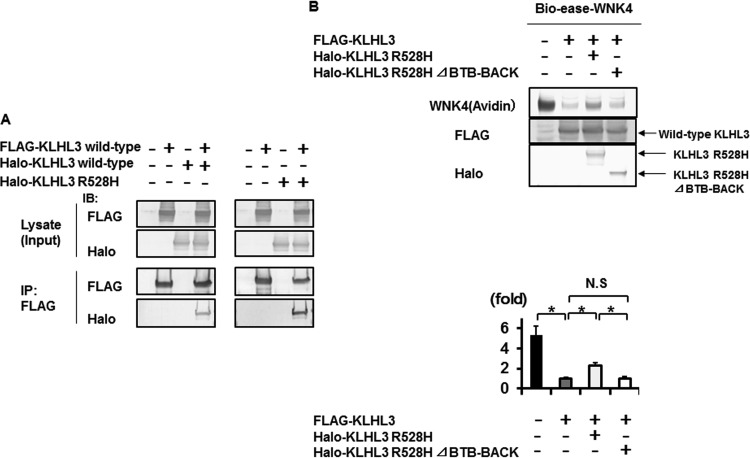
FIG 8.
Dominant negative effect of KLHL3 R528H requires dimer formation of KLHL3. (A) FLAG-tagged KLHL3 was coimmunoprecipitated with Halo-tagged KLHL3 and Halo-tagged R528H KLHL3 in HEK293T cells. Wild-type KLHL3 could form a homodimer and heterodimer with wild-type and mutant KLHL3 R528H, respectively. IP, immunoprecipitation. (B, upper panel) Coexpression experiments of KLHL3 R528H and wild-type KLHL3. Compared to the cells transfected with wild-type KLHL3 alone, the degradation of WNK4 protein was significantly decreased by the addition of KLHL3 R528H. In addition, this effect was cancelled when the BTB-BACK domain, containing the binding site for dimer formation, was deleted from the mutant KLHL3 R528H, suggesting that the dominant negative effect of mutant KLHL3 R528H required dimer formation of KLHL3. (B, lower panel) Densitometry analysis of avidin binding to Bio-ease-WNK4.