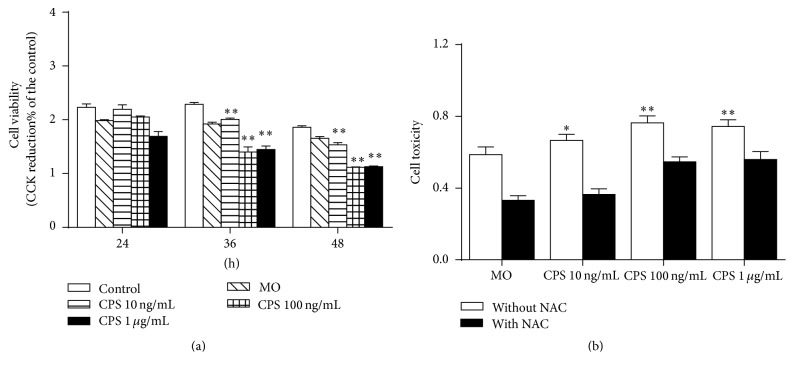
Figure 2.
Impacts of CPS on cell viability of sheep bronchial epithelial cells. (a) Cell viability treated with various concentrations of CPS was measured by a CCK assay after 24, 36, and 48 h treatment. (b) 4-week-old ALI cultures of sheep bronchial epithelial cells were apically treated with capsular polysaccharide (CPS) at 100 ng/mL or infected with M. ovipneumoniae (MO) at MOI of 30 for 48 h before samples were harvested for analysis. Cells were pretreated with/without NAC (10 mM) for 2 h, followed by exposure to indicated conditions for 48 h. Results showed that LDH release was significantly increased versus the control group and that it can be reversed by NAC. Values are mean ± SD for at least three independent experiments performed in triplicate. ∗p < 0.05 and ∗∗p < 0.01 versus control.