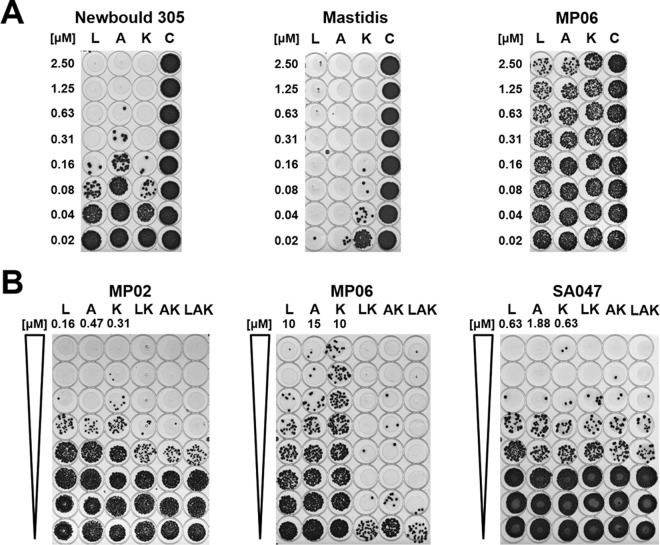
FIG 2.
Spot assays in milk with PGH constructs and different staphylococcal mastitis isolates. (A) Determination of minimum bactericidal concentrations (MBCs). Twofold serial dilutions of lysostaphin (L), Ami2638A (A), and CHAPK_CWT-LST (K) or buffer as control (C) were incubated with staphylococci (5 × 105 CFU/ml) in milk in 96-well plates for 2 h at 37°C. Aliquots of 5 μl from each well were spotted on TSB agar cast in the sterile lids of 96-well plates and incubated overnight. In each case, the PGH concentration yielding the first cleared spot was defined as the MBC. Examples for medium (S. aureus Newbould 305), high (S. aureus Mastidis), and low (S. warneri MP06) susceptibility are shown. (B) Determination of synergistic effects in milk when using mixtures of PGH constructs. Twofold serial dilutions of single enzymes and mixtures of lysostaphin and CHAPK_CWT-LST (LK), Ami2638A and CHAPK_CWT-LST (AK), and all three enzymes (LAK) were prepared in milk and tested in spot assays as described for panel A. For each individual PGH construct, the highest concentration used (i.e., the concentration in the first well) is indicated on top of the respective lane. The concentration of each enzyme in a mixture was half (for LK and AK) or one-third (for LAK) of the concentration of the respective single PGH construct in the same row. Results for S. chromogenes MP02 (synergy), S. warneri MP06 (strong synergy), and S. aureus SA047 (no synergy) are shown.