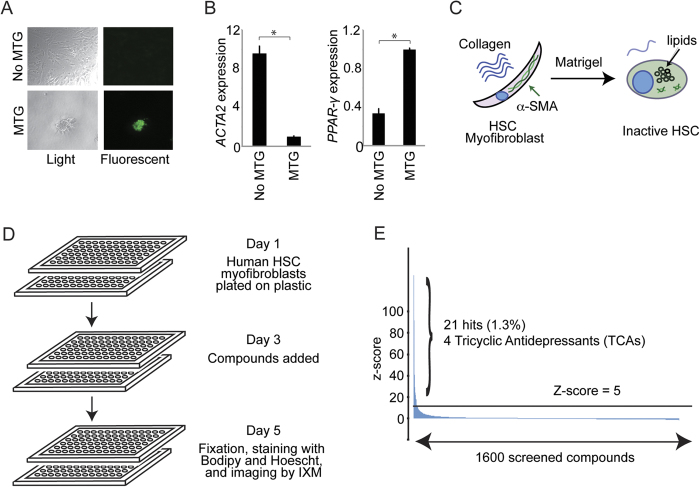
Figure 1. Design and performance of a small molecule screen to identify compounds that inhibit hepatic fibrosis.
(A) Culture in Matrigel (MTG) leads to accumulation of lipid droplets characteristic of inactive HSCs. Light microscopy images (left) are shown for HSC myofibroblasts cultured without MTG (top) and with MTG (bottom) for 3 days. Staining with Bodipy 493/503 for neutral fat (right) shows accumulation of lipid droplets (green) in HSCs cultured in MTG (lower right), and not in HSCs cultured without MTG (upper right). Images are shown at 10x magnification. (B) Quantitative real time (qRT)-PCR was performed to measure ACTA2 (left) and PPAR-γ (right) mRNA levels in HSC myofibroblasts with and without MTG for 3 days. Samples were normalized using GAPDH. *p < 0.05. (C) Culture of human HSC myofibroblasts in MTG leads to accumulation of lipid droplets and reduced expression of α-SMA (encoded by ACTA2). (D) Schematic illustrating the screen designed to identify compounds that revert HSC myofibroblasts to inactive HSCs. (E) 1600 known bioactive compounds were screened, and the Median Absolute Deviation (MAD)-based Z score (y-axis) was plotted for each compound (x-axis). The horizontal black line indicates a MAD-based Z score of 5.