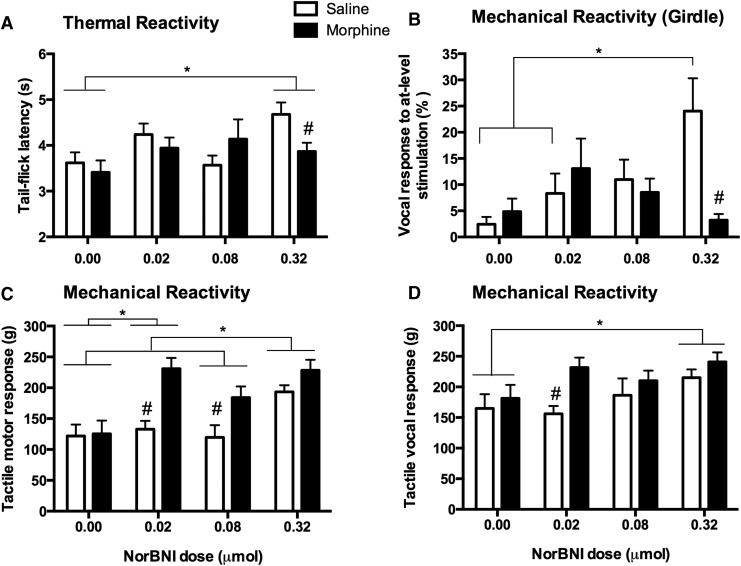
FIG. 4.
There were significant effects of nor-Binaltorphimine (norBNI) pretreatment on the long-term recovery of sensory function. At the end of the 21 day recovery period, there was a significant main effect of norBNI on thermal reactivity (A). NorBNI decreased thermal reactivity relative to subjects that were not given norBNI. By contrast, on the girdle test of at-level allodynia, there was a significant interaction between norBNI and morphine treatment (B); norBNI appeared to increase reactivity in subjects that were not treated with morphine. As found on the test of thermal reactivity, both morphine and norBNI decreased motor (C) and vocal (D) responses to tactile stimulation at day 21 post-injury. Results shown as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05 for post-hoc tests; # p < 0.05 for planned comparisons.