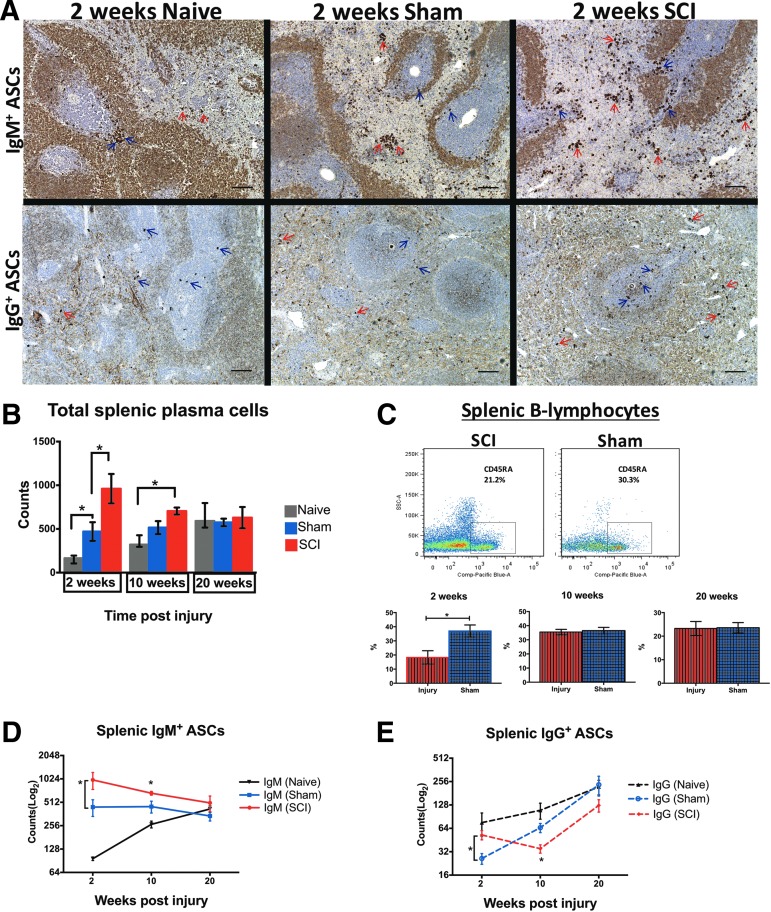
FIG. 7.
Changes in splenic antibody-secreting cell (ASC) counts following cervical spinal cord injury (cSCI). (A) Representative brightfield microscopy images showing splenic immunoglobulin M (IgM)+ and IgG+ ASCs (or plasma cells) from age-matched naïve, sham, and SCI rats at 2 weeks post-injury. Red arrows indicate ASCs in the red pulp and blue arrows show ASCs in the white pulp of the spleen. Scale bar: 100 μm. (B) Total splenic ASC counts in naïve, sham, and SCI rats at 2, 10, and 20 weeks post-injury. At 2 weeks, the cSCI group had higher plasma cell counts than sham controls. Also, sham animals had higher counts of splenic ASCs than age-matched naïve rats. There was no significant difference in total plasma cell counts at subsequent time-points between animals with cSCI and sham injury or between naïve and sham animals, although ASC counts were higher in the cSCI group than in age-matched naïve controls at 10 weeks. *p < 0.05, one-way analysis of variance for each time-point with Bonferroni post hoc test, n = 6-8/group, mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM). (C) Changes in frequency of splenic B-cells at 2, 10, and 20 weeks post-injury. Top: Representative dot plot panels showing the gated population of B-lymphocytes out of viable CD45+ cells (leukocytes) in the spleen of a spinally injured and a sham rat at 2 weeks post-injury. Bottom: Changes in percent frequencies (%) of splenic B-cells at 2, 10, and 20 weeks post-injury. B-lymphocytes declined significantly at 2 weeks post-injury, compared with shams, but recovered to normal levels at subsequent time-points. *p < 0.05, Independent Student's t-test, n = 6/group, mean ± SEM. (D-E) Quantification of IgM+ and IgG+ ASCs in the spleen of naïve, sham and SCI rats at 2, 10, and 20 weeks post-injury. Asterisks indicate significant differences between SCI and sham groups only. (D) IgM+ ASC counts increased significantly at 2 and 10 weeks post-cSCI, compared with shams. At 20 weeks, there was no significant difference between groups. (E) IgG+ ASC counts increased at 2 weeks but declined significantly at 10 weeks post-cSCI, compared with shams. IgG+ ASC counts were similar between groups at 20 weeks. Color image is available online at www.liebertpub.com/neu