Fig. 1.
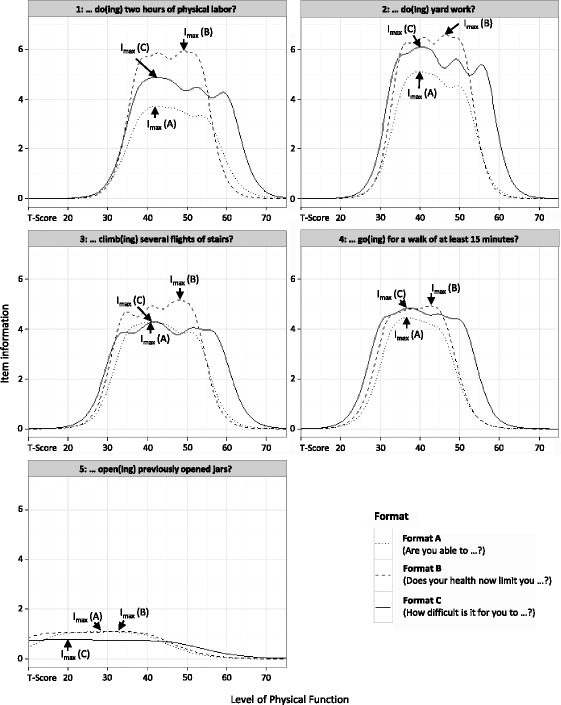
Comparison of item information functions (IIFs) using different item formats. Format A: “Are you able to …” (five-category response scale from “Without any difficulty” to “Unable to do”); format B: “Does your health now limit you in …” (five-category response scale from “Not at all” to “Cannot do”); format C: “How difficult is it for you to …” (six-category response scale from “Very easy” to “Impossible”). Item parameters and IIFs were initially estimated using a standard normal physical function (PF) metric. PF values were subsequently transformed to a T-metric, where 50 = mean and 10 = standard deviations of the analytic sample (x-axis). Item information values on the y-axis are reported unchanged. I max depicts the specific point on the T-score continuum, where a given item delivers maximum item information
