Fig. 3.
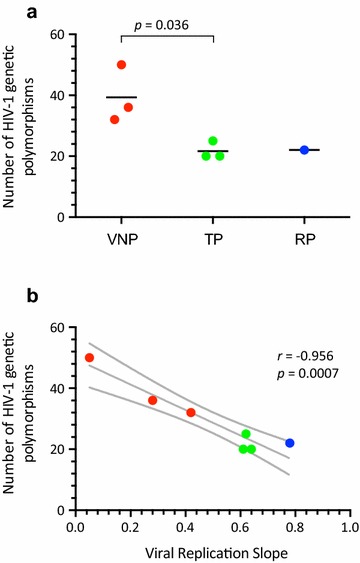
a Comparison of the number of HIV-1 genetic polymorphisms in the near full-length HIV-1 genome that have been associated with impaired HIV-1 replicative fitness and/or disease progression [11, 31, 32, 40, 42, 44–62, 77, 78] among the three groups of patients, i.e., VNP, RP, and TP. Unpaired t test was used to assess the statistical significance between VNP and TP patients. A detailed list of the mutations is included in Table 2. b Pearson correlation coefficient was used to determine the strength of association between the number of HIV-1 genetic polymorphisms and the HIV-1 replicative fitness calculated by viral growth kinetics analysis (viral replication slope) described in Fig. 1. r correlation coefficient, p two-tailed p value. Dotted lines represent 95% confidence intervals
