Fig. 3.
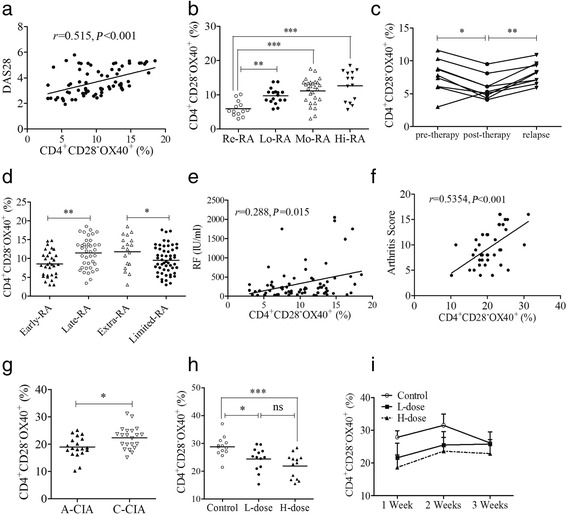
Correlations between CD4+CD28−OX40+ T cells and clinicopathological characteristics. a Correlation between DAS28 and the percentages of this subset (n = 71) in patients with RA. b Subset percentages of patients with Re-RA (n = 13), Lo-RA (n = 17), Mo-RA (n = 27), and Hi-RA (n = 14). c Changes of this subset in patients with RA treated with MTX (n = 9). d Percentages of this subset in patients with Early-RA (n = 32), Late-RA (n = 39), Extra-RA (n = 18), and Limited-RA (n = 53). e Correlation between RF levels and percentages of this subset (n = 71) in patients with RA. f Correlation between the arthritis scores of CIA mice and the percentages of this subset (n = 40). g Percentages of this subset in A-CIA (n = 19) and C-CIA (n = 21) mice. h Subset percentages in CIA mice treated with the L-dose (n = 13) or H-dose (n = 13) of Dex or PBS (n = 13). i Changes of this subset after Dex treatment. Each data point represents an individual subject; horizontal lines represent means; the r value indicates Spearman’s correlation coefficient; * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001, ns = not significant. A-CIA Acute collagen-induced arthritis, CIA Collagen-induced arthritis, C-CIA Chronic collagen-induced arthritis, Dex Dexamethasone, Extra-RA Rheumatoid arthritis with extraarticular manifestations, H-dose High dose, Hi-RA Rheumatoid arthritis with high disease activity, L-dose Low dose, Limited-RA Rheumatoid arthritis with limited joint manifestations, Lo-RA Rheumatoid arthritis with low disease activity, Mo-RA Rheumatoid arthritis with moderate disease activity, MTX Methotrexate, RA Rheumatoid arthritis, Re-RA Rheumatoid arthritis with remission, RF Rheumatoid factor
