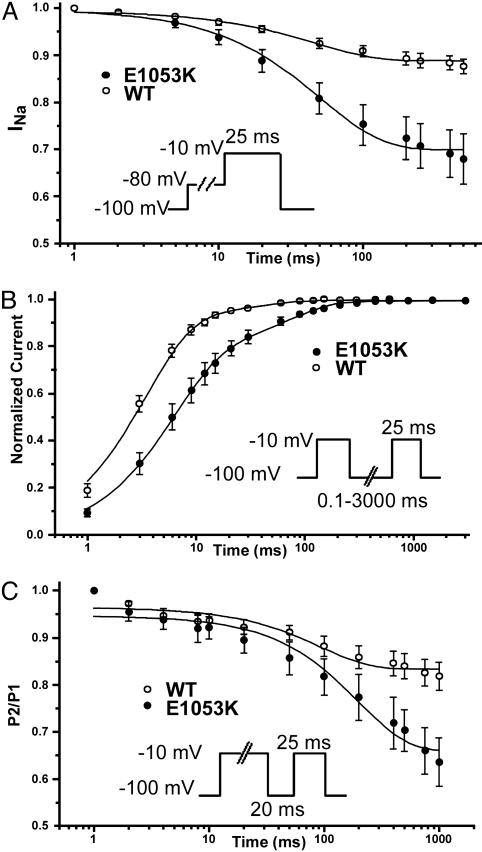
Fig. 5.
Nav1.5 E1053K displays abnormal inactivation properties compared to WT Nav1.5. (A) The transition in the close-state inactivation is favored for the E1053K mutant channel respect to WT (n = 13 for WT, n = 11 for E1053K). (B) The recovery from fast inactivation is slower in the E1053K channel compared to the WT channel (n = 9 for WT, n = 6 for E1053K). (C) Enhancement of the intermediate inactivation state for Nav1.5 E1053K compared to WT Nav1.5 (n = 10 for WT, n = 5 for E1053K). After 200 ms, there is 64% available for E1053K vs. 83% of the WT. In each panel, see Inset for protocol.