Table 2. Optimization of reaction conditions.
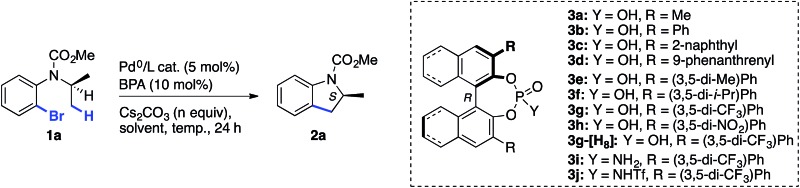
| |||||||
| Entry | BPA | Catalyst a | n | Solvent | Temp. (°C) | e.r. of 2a b | Yield of 2a c (%) |
| 1 | 3a | Pd(PCy3)2 | 1.5 | Xylenes | 140 | 52 : 48 | 80 |
| 2 | 3b | Pd(PCy3)2 | 1.5 | Xylenes | 140 | 50 : 50 | 65 |
| 3 | 3c | Pd(PCy3)2 | 1.5 | Xylenes | 140 | 54 : 46 | 68 |
| 4 | 3d | Pd(PCy3)2 | 1.5 | Xylenes | 140 | 52 : 48 | 71 |
| 5 | 3e | Pd(PCy3)2 | 1.5 | Xylenes | 140 | 57 : 43 | 39 |
| 6 | 3f | Pd(PCy3)2 | 1.5 | Xylenes | 140 | 56 : 44 | 45 |
| 7 | 3g | Pd(PCy3)2 | 1.5 | Xylenes | 140 | 80 : 20 | 50 |
| 8 | 3h | Pd(PCy3)2 | 1.5 | Xylenes | 140 | 57 : 43 | 50 |
| 9 | 3g-[H8] | Pd(PCy3)2 | 1.5 | Xylenes | 140 | 50 : 50 | 63 |
| 10 d | 3g | Pd(PCy3)2 | 1.5 | Xylenes | 120 | 87 : 13 | 24 |
| 11 | 3g | Pd(PCy3)2 | 3 | Xylenes | 120 | 84 : 16 | 56 |
| 12 | 3i | Pd(PCy3)2 | 3 | Xylenes | 120 | 84 : 16 | 50 |
| 13 | 3j | Pd(PCy3)2 | 3 | Xylenes | 120 | 55 : 45 | 15 |
| 14 | 3g | Pd(PCy3)2 | 3 | DME e | 120 | 96 : 4 | 86 |
| 15 | — | Pd(PCy3)2 | 3 | DME e | 120 | — | 29 |
| 16 | 3g | Pd2(dba)3 | 3 | DME e | 120 | — | <2 f |
| 17 | 3g | Pd2(dba)3/PCy3 | 3 | DME e | 120 | 95 : 5 | 61 |
| 18 | 3g | Pd2(dba)3/PPh3 | 3 | DME e | 120 | 91 : 9 | <20 f |
| 19 | 3g | Pd2(dba)3/PCyp3 | 3 | DME e | 120 | 97 : 3 | 24 |
| 20 | 3g | Pd2(dba)3/P(t-Bu)2Me | 3 | DME e | 120 | 97 : 3 | <20 f |
a5 mol% Pd(PCy3)2 (entries 1–15) or 2.5 mol% Pd2dba3/10 mol% PR3 (entries 16–20).
bEnantiomeric ratio measured via HPLC using a chiral stationary phase.
cYield of isolated product.
dReaction time: 40 h.
eWith 4 Å powdered molecular sieves.
fEstimated based on GCMS ratio. DME = 1,2-dimethoxyethane.
