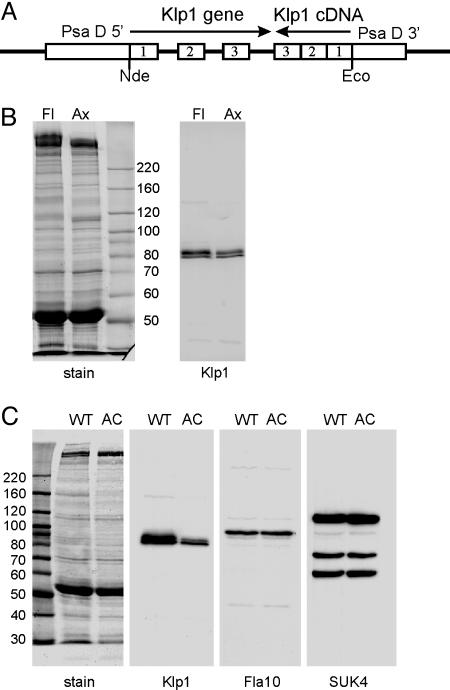
Fig. 3.
Axonemes of knockdown strains have reduced levels of Klp1. (A) Plasmid used for RNAi-mediated knockdown of Klp1. Portions of the Klp1 gene and cDNA were joined in opposite orientations and inserted into an expression plasmid containing the promoter and untranslated regions from the Chlamydomonas PsaD gene. Transcription and splicing should generate a double-stranded hairpin RNA. (B) SDS/PAGE of knockdown strain AC30 flagella (Fl) and axonemes (Ax). Gels were stained with Coomassie blue (stain) or blotted and probed with anti-Klp1 (Klp1). The blot shows that the residual Klp1 in knockdown strains is tightly associated with the axoneme. (C) Blots of wild-type (WT) and AC30 (AC) axonemes were stained with amido black (stain) or probed with anti-Klp1, anti-Fla10, or pan-kinesin antibody SUK4. Klp1 levels are reduced by 80% in AC30 axonemes, whereas other axonemal kinesin levels are unchanged. The sizes (in kDa) of molecular mass standards are indicated next to each stained panel.