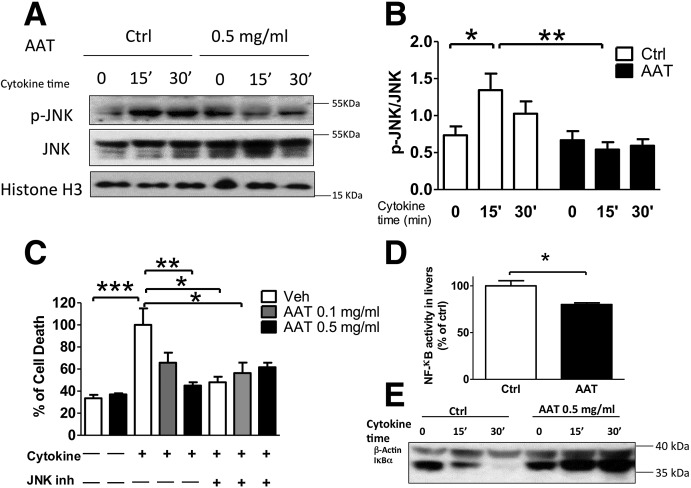
Figure 5.
AAT protects islets from cytokine-induced cell death by suppression of JNK phosphorylation and NF-κB activation. AAT treatment reduces p-JNK after cytokine treatment as measured by Western blot. A: Representative immunoblot of p-JNK and total JNK and histone H3 by Western blot. B: Ratio of p-JNK to total JNK from immunoblots quantified by densitometry. Data are presented as mean ± SD for five individual experiments. C: Cell death measured in βTC3 cells pretreated with AAT at 0.1 mg/mL or 0.5 mg/mL and/or 20 nmol/L SP600125, the JNK phosphorylation blocker (JNK inh), for 1 h and stimulated with cytokines for 48 h using the Cell Death ELISA kit. Experiments were repeated four times. Data are presented as mean ± SD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 using one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey post hoc analysis. D: NF-κB activity (percentage to control [Ctrl]) as measured by p65 level in the nuclear fraction by ELISA in livers bearing islet grafts. Experiments were repeated three times. E: Representative immunoblot of inhibitor of κB-α (IκBα) and β-actin in βTC3 cells pretreated with vehicle or 0.5 mg/mL AAT, and stimulated with cytokine for 0–30 min as analyzed by Western blot. *P < 0.05 AAT vs. Ctrl by Student t test.