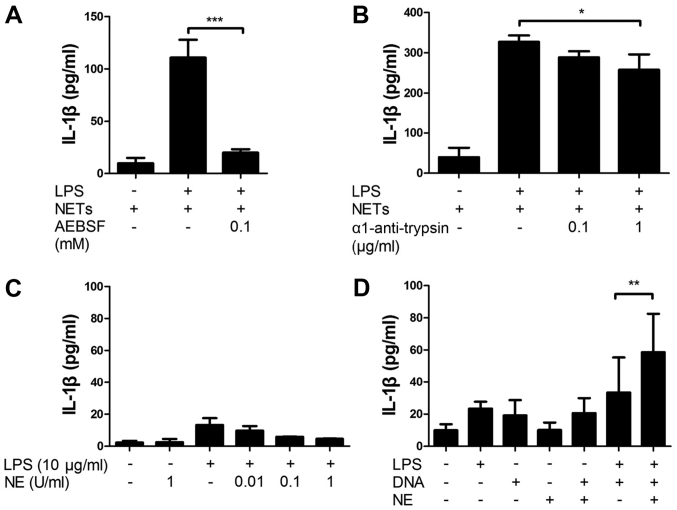
Figure 6.
Involvement of neutrophil extracellular trap (NET)-associated serine proteases in the NET/lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced interleukin (IL)-1β production. J774 cells were (2×104 cells) treated with LPS (10 ng/ml) and NETs (1.7×105 cell equivalents) for 24 h in 100 µl RPMI-1640 medium in the absence or presence of serine protease inhibitors: (A) AEBSF or (B) α1-anti-trypsin. Thereafter, the supernatants were recovered for the assays of IL-1β. Data show the means ± standard deviation (SD) of 3-5 separate experiments. Values are compared between the NET/LPS treatment in the absence and presence of serine protease inhibitors. J774 cells (2×104 cells) were treated with (C) LPS (10 ng/ml) and neutrophil elastase (NE) (0.01 and 0.1 U/ml) in 100 µl RPMI-1640 medium for 24 h. Otherwise, J774 cells were treated with (D) LPS (10 ng/ml), NE (0.1 U/ml), CT-DNA (1 µg/ml) or their combinations for 24 h. Thereafter, the supernatants were recovered for the assays of IL-1β. Data show the means ± SD of 3–6 separate experiments. Values are compared between the LPS/DNA and LPS/DNA/NE. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.