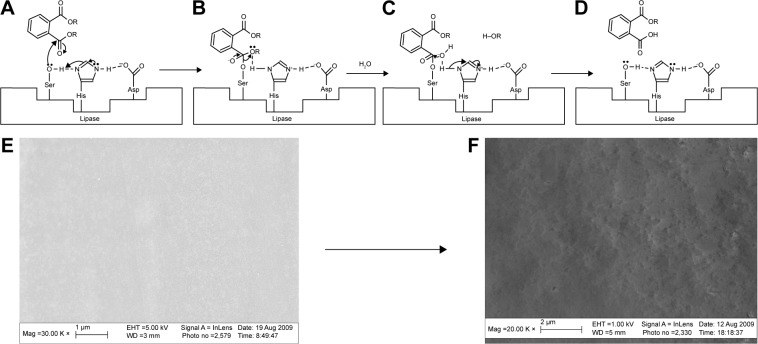
Figure 1.
Proposed mechanism for hydrolysis of a plasticizer by Rhizopus arrhizus lipase.
Notes: (A) Phthalate binds to the lipase molecule and the active site of the lipid (Ser O−) and performs a nucleophilic attack of the substrate’s carbonyl carbon atom. (B) A transition state occurs where a covalent intermediate is formed by binding of the substrate to the enzyme’s serine residue. (C) A water molecule is activated by the histidine residue of the lipase and performs a nucleophilic attack on the intermediate. (D) The products of the reaction are released. (E) SEM image of unetched PVC ETT: magnification ×30 K. (F) SEM image of PVC ETT etched with a 0.1% R. arrhizus solution (nano-R): magnification ×20 K.
Abbreviations: ETT, endotracheal tube; PVC, polyvinyl chloride; SEM, scanning electron microscopy.