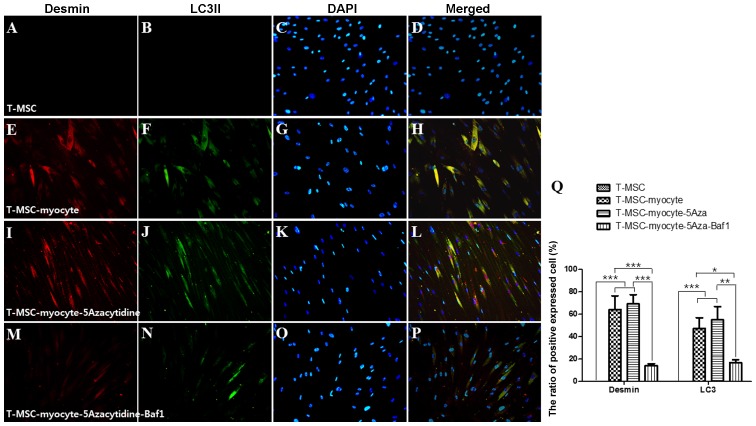
Figure 6.
Effect of 5Aza and Baf1 on the skeletal myogenic differentiation of human T-MSCs. The expression of desmin and LC3II (green) in the T-MSCs (A–D) during the process of myogenic differentiation [T-MSC-derived myocytes; (E–H)]. The role of autophagy was evaluated with an inducer, 5Aza [T-MSC-derived myocytes-5-azacytidine (I–L)], and an inhibitor, Baf1 [T-MSC-derived myocytes-5-azacytidine-Baf1 (M–P)], during skeletal myogenic differentiation. The cells were counterstained with DAPI (blue). The samples were analyzed under a fluorescence microscope using appropriate filters. Original magnification, ×200. (Q) The ratio of cells immunoreactive for anti-desmin and anti-LC3. Data are expressed as means ± SEM. For each condition, four slides were used for quantification. Graphs represent the average of multiple tests from three independent experiments. 5Aza, 5-azacytidine; Baf1, bafilomycin A1; LC3II, microtubule-associated protein 1A/1B-light chain 3; Baf1, bafilomycin A1; T-MSCs, tonsil-derived mesenchymal stem cells.