FIGURE 2. Increased PMN, oxidation injury and inflammatory responses in lungs of ogg-1 KO mice.
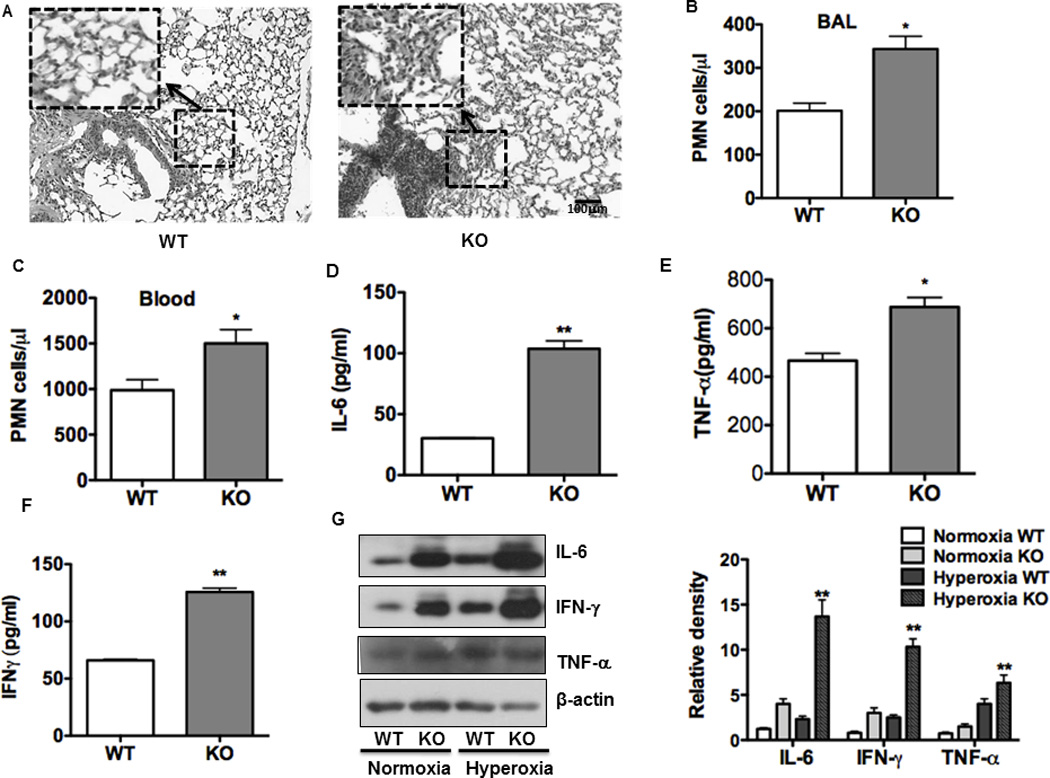
(A) Hyperoxia increased lung injury and inflammation as assessed by H&E staining. (B) and (C) Increased PMN infiltration and an acute inflammatory response were observed in the lung (B) and blood (C) of ogg-1 KO mice compared to WT mice (n=6) following hyperoxia for 48 h. (D)–(F), Increased inflammatory cytokines in BAL fluid of ogg-1 KO mice compared to those of WT mice by ELISA. (G) Increased expression of inflammatory cytokines in lungs of ogg-1 KO mice compared to WT mice by immunoblotting analysis. ogg-1 KO mice and WT mice were exposed to hyperoxia (95%) for 48 h. Gel data were quantified using ImageJ densitometry. Data were representative of three experiments with similar results (student t-test, *p< 0.05, **p< 0.01).
