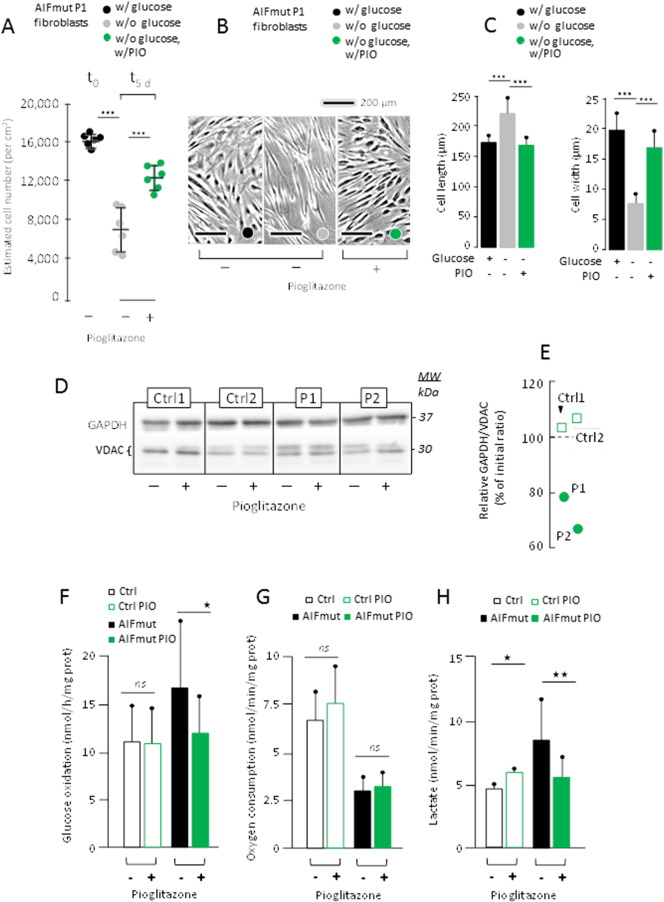
Fig. 6.
PIO-treated cultured fibroblasts derived from AIF mutant patients and grown in the absence of glucose, have decreased GAPDH expression and lower glucose utilization.
(A) Effect of 5 days of 10 μM PIO treatment (0.1% DMSO final) on AIF mutant (AIFmut) P1 fibroblast number. Noticeably under the used conditions (i.e. absence of glucose), skin fibroblasts derived from control individual roughly double their number in 3–4 days depending on individual (not shown). (B) Light microscopy (× 4) of P1-derived cultured fibroblasts grown in the presence of glucose (left panel; black label), in the absence of glucose (middle panel; grey label) or in the absence of glucose but presence of 10 μM PIO (0.1% DMSO final; left panel; grey label). (C) Estimate of length (left panel) and maximal width (right panel) of P1-derived AIF mutant fibroblasts grown as in (B) in the presence (black bars), or absence (grey bars) of glucose, or in the absence of glucose but presence of PIO (green bars). (D) Effect of PIO on GAPDH expression in two controls and the two AIF-mutant P1 and P2 skin fibroblasts grown in the presence of glucose. VDAC was indicated as a loading control. (E) Effect of PIO in the presence of glucose on GAPDH/VDAC ratios in the 2 controls (Green open squares) and the P1 and P2 patients (green circles). GAPDH/VDAC ratios in the presence of PIO were expressed as a percent of initial ratio measured in the absence of PIO. (F) Mean ± 1 SD of C14 glucose oxidation, oxygen uptake (G), and lactate excretion (H) by control skin fibroblasts in the absence (black open bars) or presence (green open bars) of PIO or by AIF-mutant patient fibroblasts in the absence (black bars) or presence (green bars) of PIO. Cells counting, cell length and width estimation, biochemical analyses and statistical tests as described under Materials and Methods.