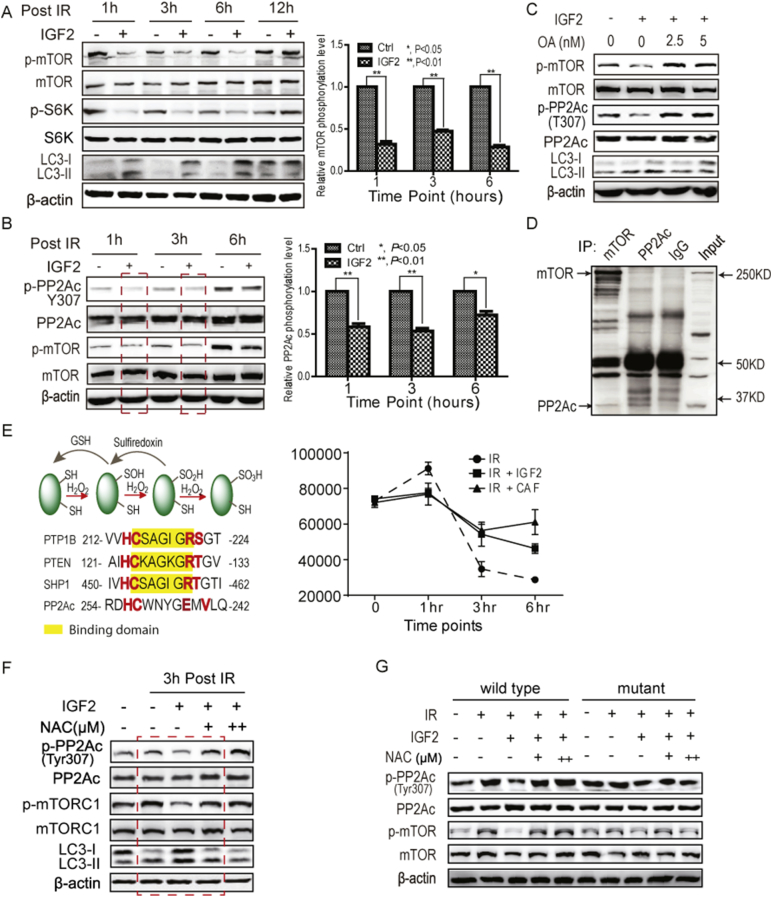
Fig. 4.
CAFs suppressed mTOR activity through increasing PP2A activity in irradiated cancer cells. A. IGF2 suppressed mTOR activity in A549 cells post-radiation. A549 cells were treated with 2 Gy of radiation with or without 50 ng/mL of IGF2. B. IGF2 increased the activity of PP2A. PP2A activity was reflected by the dephosphorylation of T307 in A549 cells at 3 h post-radiation. The concentration of IGF2 was 50 ng/mL. C. The PP2A inhibitor, okadaic acid, restored IGF2-induced mTOR suppression post-radiation. D. The PP2Ac was associated with mTOR. The reciprocal co-immunoprecipitations were performed. E. IGF2 maintained the redox homeostasis in A549 cells post-radiation. The levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) were analyzed by 2′,7′-dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate flow cytometry analyses of A549 cells post-radiation (2 Gy). F. The antioxidant N-acetylcysteine (NAC) abolished the IGF2-promoted PP2A activity. The concentration of NAC was 0.25 mM/mL (+) and 0.5 mM/mL (++), respectively. G. ROS regulated PP2A activity through the oxidation of Cys 251. The Cys 251 of PP2Ac was mutated to serine. The PP2A activity was analyzed at 3 h post-radiation. The concentrations of IGF2 and NAC were the same as described above.