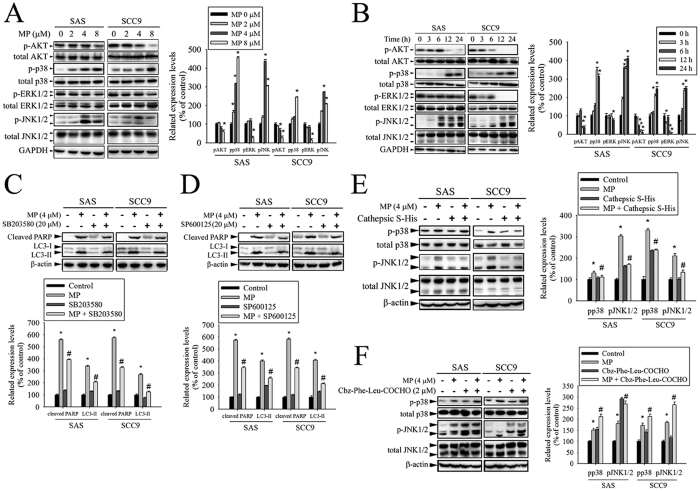
Figure 6. CTSS blocked the effects of MP on p38 MAPK and JNK1/2 in SAS and SCC9 cells.
(A) Cells were treated with different concentrations of MP (0–8 μM) for 24 h. The p-AKT, p-p38, p-ERK1/2, and p-JNK1/2 were analyzed by Western blot with their respective antibodies. The total protein of AKT, p38, ERK1/2, and JNK1/2 is also shown. The intensity of the phosphorylation signals was determined by densitometry and normalized to their total protein levels (right panel). (B) Cells were treated with MP (8 μM) for indicated time intervals and the phosphorylation status and total levels of proteins were measured by Western blot. Quantitative analyses of the phosphorylation status and total levels of proteins are shown in the right panel. (C,D) Effects of the inhibition of p38 MAPK and JNK1/2 on MP-induced apoptosis and autophagy were assessed by Western blot using specific antibodies (cleaved PARP and LC3-I/LC3-II). Cells were pretreated with SB203580 (p38 MAPK inhibitor, 10 μM) or SP600125 (JNK inhibitor, 20 μM) for 1 h followed by treatment with or without MP for 24 h. Band intensity was quantified by densitometry analysis. β-actin was used as an internal control to normalize the amount of proteins (Bottom panel). (E,F) The effects of CTSS overexpression or CTSS inhibitor on MP-induced activation of p38 MAPK and JNK1/2 were assessed by Western blot. Quantitative analyses of the phosphorylation status and total levels of proteins are shown in the right panel. Values represent the mean ± SD of 3 independent experiments. *P < 0.05 vs. control (cells treated with DMSO only), and #P < 0.05 vs. MP.