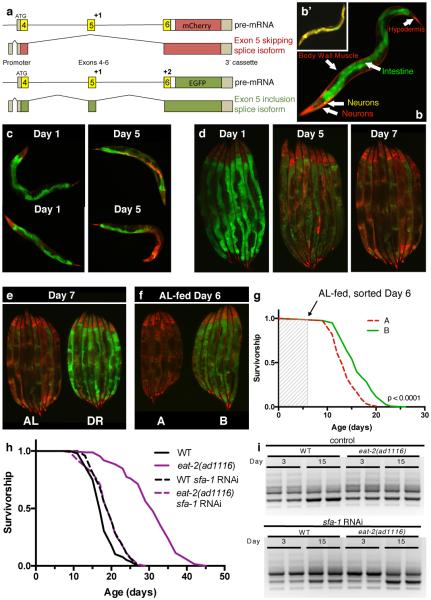
Figure 1. The role of RNA splicing in DR longevity.
a, ret-1 splicing reporter schematic12. b, Tissue-specific ret-1 splicing in day 1 C. elegans. b’, Control reporter without frameshifts. c, Representative reporter splicing at days 1 and 5, and d, days 1, 5, and 7. e, Splicing reporter worms on AL or DR at day 7. f, Representative images of age-matched animals in group A (increased exon 5 skipping) and group B (increased exon 5 inclusion). g, Survival of groups A and B. Arrow denotes sorting day (1 of 2 replicates). h, Survival of WT and eat-2(ad1116) animals +/− sfa-1 RNAi (7 replicates). i, tos-1 isoforms in WT worms and eat-2(ad1116) +/− sfa-1 RNAi (day 3 vs. 15, n=2 biological replicates). Lifespans: n=100 worms/condition; p values: log-rank test.