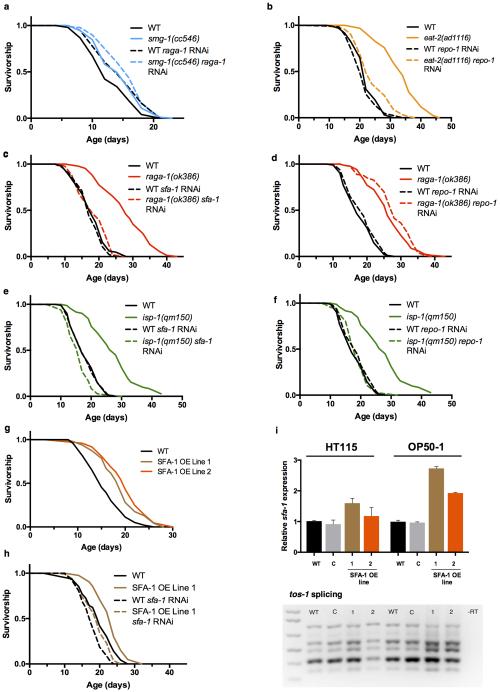
Extended Data Figure 9. Differential effects of sfa-1 and repo-1 knockdown in multiple longevity pathways.
a, Effect of raga-1 RNAi in nonsense mediated decay defective smg-1(cc546) mutant worms (p=0.041 RNAi treatments, lifespan at 24°C). b, Survival of WT and (eat-2(ad1116)) on repo-1 RNAi (p<0.0001, vs. WT+repo-1 RNAi). c, sfa-1 RNAi blocks RAGA-1 mediated longevity (p=0.2181, Gehan-Breslow-Wilcoxon test). d, repo-1 RNAi has no effect on raga-1(ok386) longevity (p<0.0001). e, Effect of sfa-1 RNAi on mitochondrial ETC mutant isp-1(qm150) mediated longevity (p=0.004). f, repo-1 RNAi shortens isp-1(qm150)-mediated longevity to WT levels (p=0.4951). g, Effect of SFA-1 overexpression on WT lifespan on OP50-1 bacteria (p<0.0001 both lines). h, Survival analysis of WT and SFA-1 overexpression lines on sfa-1 RNAi (p=0.0042). i, Top: Monitoring of sfa-1 levels by qRT-PCR (C: injection marker control line; 1, 2: SFA-1 overexpression lines, error bars mean ± SD of 2 biological replicates for strains grown on HT115 bacteria (left), error bars are mean ± SD of 2 technical replicates for strains grown on OP50-1 bacteria (right)) Bottom: tos-1 isoform ratios with SFA-1 overexpression in day 1 adults. p values survival analysis by log-rank test.