Figure 1.
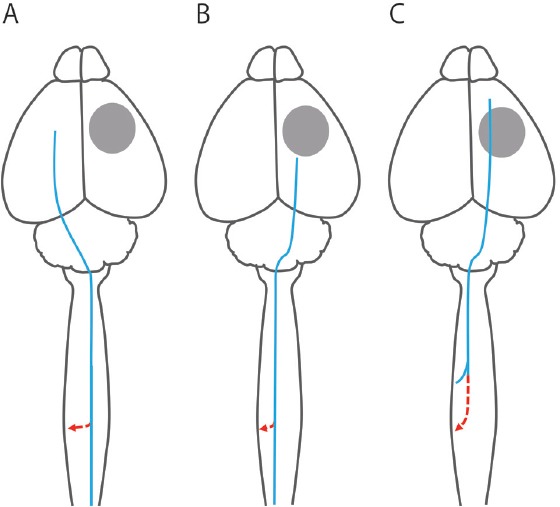
Type of axonal remodeling in the corticospinal tract.
The type of axonal remodeling in the corticospinal tract can be distinguished by comparing the original projection of the corticospinal axon and the newly formed one. The gray circle, the blue line, and the red line indicate the stroke lesion, original corticospinal axon, and newly formed corticospinal axon, respectively. The first type of axonal remodeling (A) is the recrossing of the corticospinal axon projecting from the contralesional hemisphere to the ipsilesional spinal cord which innervate forelimb or more caudal body part. The majority of previous studies investigating axonal remodeling after stroke have demonstrated this type of axonal remodeling. The second type of axonal remodeling (B) is the collateral formation from the corticospinal axon projecting from the ipsilesional hemisphere to the contralesional (affected) body part caudal to the area where a new axon is formed (e.g., hindlimb: Starkey et al., 2012). The third type of axonal remodeling (C) is the collateral formation accompanied by axonal extension in the dorsal column from the ipsilesional hemisphere to the contralesional body part rostral to the area where a new axon is formed (e.g., trunk: Okabe et al., 2016).
