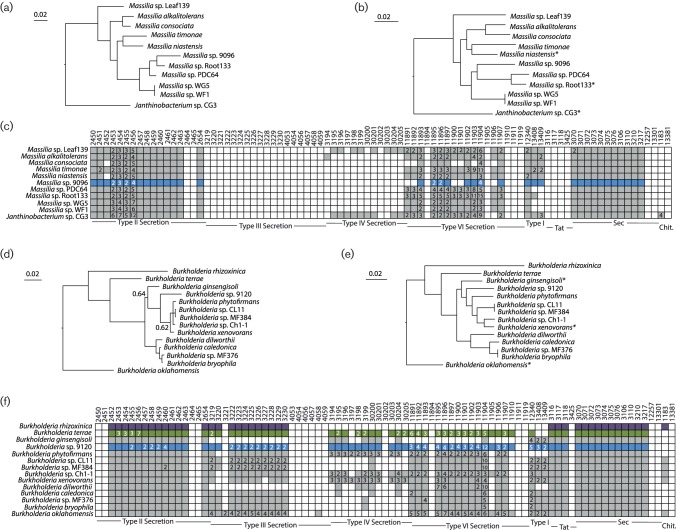
Fig. 2.
Phylogenetic analysis and comparison of interdomain interaction systems for Massilia and Burkholderia. (a, d) Bayesian phylogenies for focal EHB and non-EHB strains for Massilia (a) or Burkholderia (d) were built from concatenated sequences of RpoD and GyrB. Unless noted, posterior probabilities at all nodes are >0.95. (b, e) Maximum-likelihood phylogenies for EHB and non-EHB strains were inferred from whole-genome sequences using RealPhy for Massilia (b) or Burkholderia (e). (c, f) KEGG pathway searches were implemented in IMG to identify bacterial pathways known to be involved in signalling between bacteria and eukaryotes for Massilia (c) or Burkholderia (f). Genomes queried for each clade are listed across the y-axis. Boxes along the x-axis indicate KEGG pathway identifiers (top) for constituent genes for each bacteria secretion system with grouping by system (bottom). Coloured/filled boxes indicate that at least one gene within the genome is present and classified according to that specific KEGG identifier. Numbers inside the coloured/filled boxes denote that more than one gene within that genome is classified according to that KEGG identifier. Boxes for EHB bacteria described in this report are coloured blue. Those for a previously described EHB (B. rhizoxinica [14]) or bacteria demonstrated to interact with fungi (B. terrae [54]) are coloured purple and green, respectively. * Indicates that these genomes were used as references for building phylogenies using RealPhy.