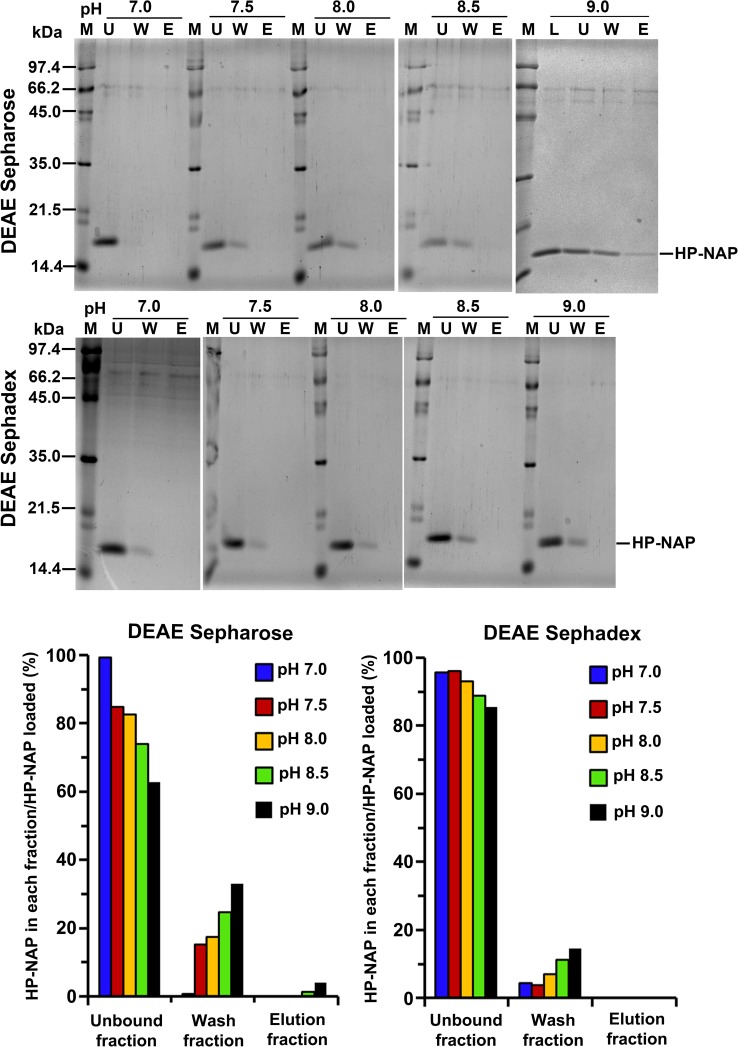
Fig 4. Binding ability of HP-NAP purified from DEAE negative mode chromatography to DEAE resins at pH 7.0 to 9.0.
The purified recombinant HP-NAP obtained from the unbound fraction of DEAE Sepharose and DEAE Sephadex resins from the batch chromatography at pH 7.0 to 9.0 at 25°C was re-subjected to the batch chromatography under the same conditions as described in Materials and Methods to examine the binding ability of pure HP-NAP to the two DEAE resins. The unbound (U), wash (W) and elution (E) fractions were analyzed by SDS-PAGE on 15% gels. Molecular masses (M) in kDa are indicated on the stained gels. The percent ratio of the amount of recombinant HP-NAP detected in each fraction to the amount of HP-NAP loaded on the resin at each pH was calculated from the intensity of HP-NAP band on SDS gels for each fraction divided by the sum of those for the unbound, wash and elution fractions. Similar results were obtained from at least two to three independent experiments. Note: The purified recombinant HP-NAP obtained from the unbound fraction from DEAE negative mode chromatography at 9.0, indicated as load (L), is shown.