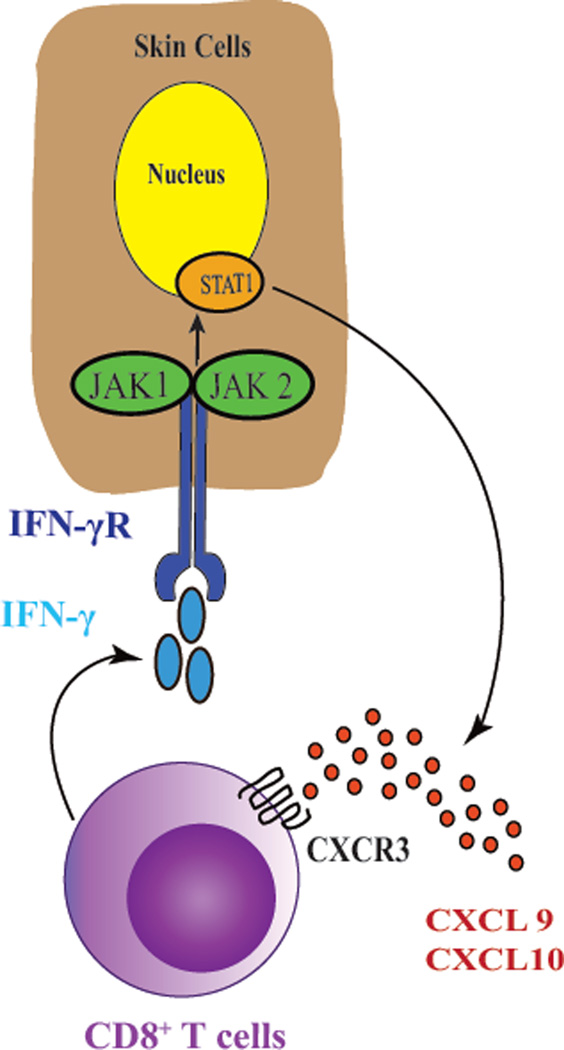
Fig. 2.
Autoimmunity in vitiligo is driven by the IFN-γ-CXCL10 cytokine signaling pathway. Activated melanocyte-specific CD8+ T cells secrete IFN-γ, which signals through the IFN-γ receptor (IFN-γR) to activate JAK1/2 and STAT1. This induces the production of CXCL9 and CXCL10, which signal through their receptor CXCR3 to recruit more autoreactive T cells to the epidermis, resulting in widespread melanocyte destruction. Targeting this cytokine pathway represents an emerging treatment strategy for vitiligo.