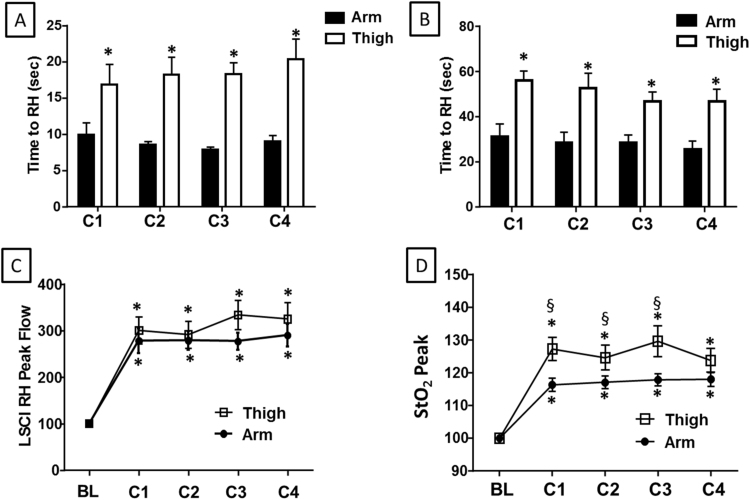
Fig. 2.
RIC to the arm or thigh causes reactive hyperemia (RH) and increased tissue oxygen delivery by StO2. The time to (A) peak blood flow (measured by LSCI) and (B) peak tissue oxygen saturation after RIC applied to either the arm (black bars) or thigh (white bars). Peak (C) blood flow and (D) tissue oxygenation after each cycle of RIC (C1-C4) applied to the arm (closed circles) or thigh (open squares). All measurements are normalized to the baseline (BL) for the respective appendage. (A–B) *p<0.01 versus arm measurement for the same cycle. (C–D) *p<0.01 versus baseline measurement. §p<0.05 for thigh versus arm. N=10. All data are mean±SEM.