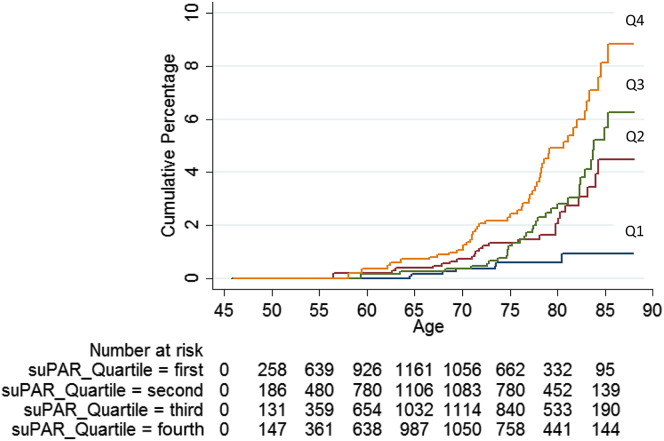
Figure 3.
Cumulative incidence of hospitalization due to impaired renal function (main diagnosis, n = 110) during follow-up according to the quartiles of suPAR in 5129 participants in the Malmö Diet and Cancer Study-Cardiovascular Cohort. In the final model, male sex (HR: 2.53; 95% CI, 1.69–3.79), BMI (HR: 1.10; 95% CI, 1.05–1.15), baseline glucose (HR: 1.21; 95% CI, 1.14–1.30), AHT (HR: 1.59; 95% CI, 1.05–2.41), eGFR (HR: 0.96; 95% CI, 0.95–0.98), and current smoking (HR: 2.23; 95% CI, 1.34–3.73) were significantly associated with hospitalization due to impairment of renal function, in addition to suPAR. The Kaplan-Meier plot shows cumulative percentages of main cases of impaired renal function during follow-up in quartiles: first (lowest values) to fourth (highest values) quartile of the baseline suPAR concentration. Median (range) concentrations of the quartiles 1 to 4 are shown in Table 2. The numbers at risk are shown at 5-year intervals. Cox regression adjusted for sex, fasting glucose levels, eGFR, BMI, systolic blood pressure, smoking status (current, former, or never smokers), and use of antihypertensive treatment (AHT) (yes/no) at baseline. Age was used as an underlying time variable. BMI, body mass index; CI, confidence interval; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; HR, hazard ratio; suPAR, soluble urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor.