Figure 1.
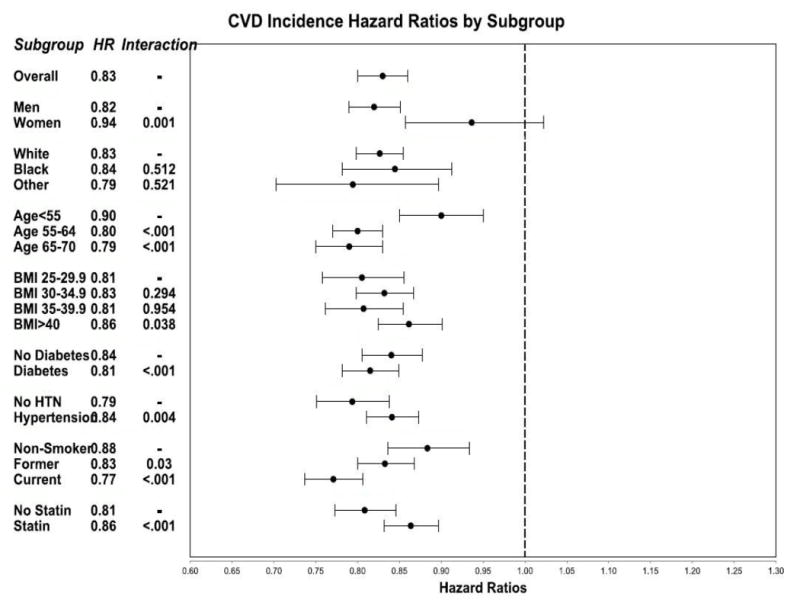
Hazard ratios for total CVD incidence among participants compared to non-participants, by subgroup, VA 2005-2012.
Notes: *N=1,463,003. Multivariable Cox proportional hazards models included covariates, in addition to those listed above: Charlson Comorbidity Index, dyslipidemia, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, prescriptions for weight loss, prescriptions with a risk of weight gain, disability status, osteoarthritis, kidney disease, sleep apnea, mental health conditions, marital status, distance to MOVE! clinic, number of primary care visits per year, and years of care in the VA system. Wald p-values for interaction terms are shown. Hazard ratios less than 1 (to the left of the dashed axis) indicate that MOVE! participation was associated with reduced CVD incidence. Significant p-values indicate possible heterogeneity of effects across subgroups.
VA, Veterans Health Administration; CVD, cardiovascular disease; HR, hazard ratio; HTN, hypertension
