Figure 6. KLK6 readily cleaves fibrilar α-synuclein species.
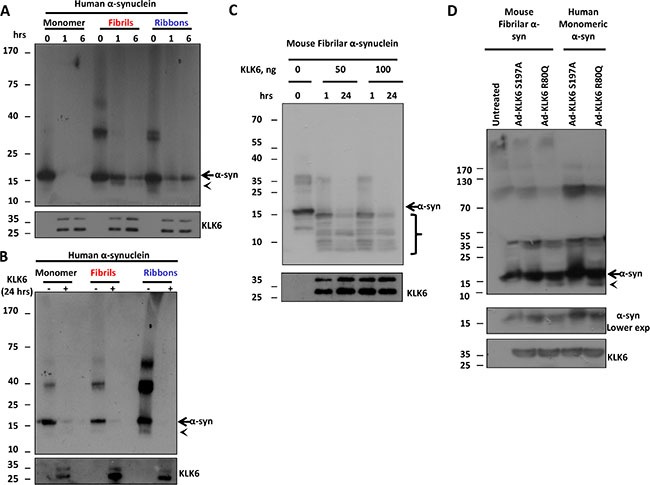
(A) 250 ng of human recombinant α-synuclein (monomer, fibrils and ribbons) were incubated with 19 ng of the recombinant active (R80Q) form of KLK6 for 0, 1 and 6 hours at 37°C. Samples were subjected to electrophoresis and α-synuclein degradation was examined by immunoblotting using the syn-1 antibody. (B) The same reaction as in A was performed for 24 hours and samples were analyzed as above. (C) 250 ng of mouse recombinant fibrilar α-synuclein was incubated with 50 ng and 100 ng of the recombinant active (R80Q) form of KLK6 for 1 and 24 hours at 37°C. Samples were analyzed as described in (A). (D) Adenoviral vectors (50 MOI) that drive the expression of constitutively active KLK6 R80Q or inactive KLK6 S197A were used to transduce primary neuronal cortical cultures prepared from wt mice. 72 hours post-infection, CM were collected, concentrated (50-fold concentration) and incubated with 250 ng of mouse recombinant fibrilar α-synuclein for 24 hours at 37°C. The presence of α-synuclein proteolytic fragments was assessed by immunoblotting, using the (C-20)-R antibody. The presence of KLK6 in the reactions was verified by using the KLK6 antibody. Arrows indicate full size α-synuclein, arrowheads and brackets indicate α-synuclein proteolytic fragments.
