Figure 4. Transcriptional inhibition of miR-27a by RARα in ATRA-induced Hep2 cells.
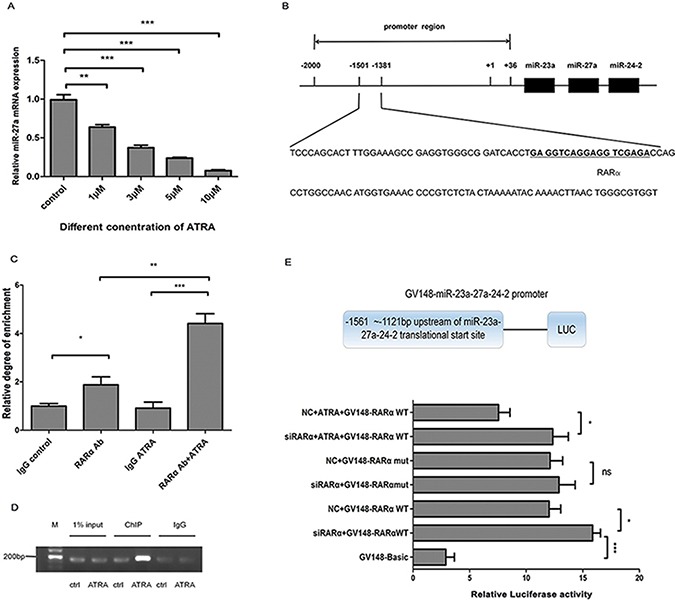
(A) miR-27a expression in different dosage of ATRA in Hep2 cells. Mature miR-27a was detected using RT-qPCR. U6 snRNA was used for the internal control. (B) Predicted RARα binding site within the miR-27a gene promoter region. (C) ChIP-qPCR analysis of RARα binding to the miR-27a gene promoter region. (D) ChIP-traditional PCR analysis of RARα binding to the miR-27a gene promoter region in ATRA-induced Hep2 cells. DNA immunoprecipitated by anti-RARα antibody from Hep2 cells after treatment with ATRA for 48 h was amplified by PCR to examine abundance of the target sequence. Input DNA and isotope-matched anti-IgG (anti-immunoglobulinG) antibody was used as controls, respectively. (E) Effect of RARα on miR-27a transcription activity by Luciferase Reporter assay. GV148-miR-27a wild/mutant promoters, Renilla luciferase plasmids and si-RARα/NC small RNAs were cotransfected into Hep2 cells, respectively. Data were expressed as the mean ± SD from at least three independent experiments. *, **, *** and ns represent p < 0.05, p < 0.01, p < 0.001 and no significance, respectively.
