Figure 7. MC3181 causes a persistent decrease of JNK/p38 phospho-activation and of the expression of proteins involved in melanoma invasion.
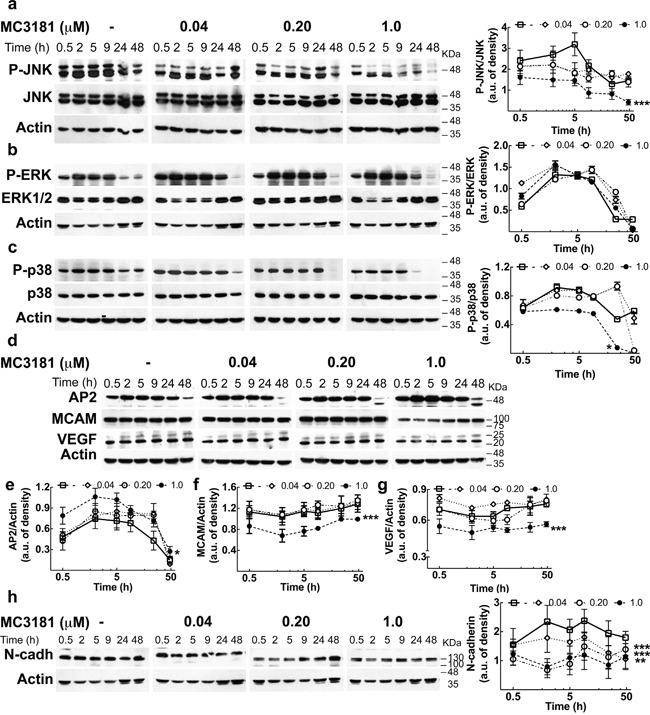
Immunoblot and densitometric analysis of a. P-JNK, b. P-ERK, c. P-p38 in absence (-□-) and in presence of MC3181 0.04 μM (-◊-), 0.20 μM (-○-) and 1.0 μM (-●-). The data revealed a significant decrease of P-JNK after only 30 minutes treatment with 1.0 μM MC3181 (***P < 0.0005 vs control). A sustained decrease of the phospho-active form of p38 was also observed at the highest MC3181 concentration (1.0 μM, *P < 0.05 vs control). Immunoblot of d. AP-2, MCAM/MUC18 (CD146) and VEGF. Actin was used as loading control. Densitometric analysis revealed a prolonged (up to 24 hours) increase of e. AP2 expression after treatment with 1.0 μM MC3181 (*P < 0.05 vs control) that paralleled the persistent decrease of the expression levels of f. MCAM/MUC18 and g. VEGF (***P < 0.0005 vs control) caused by 1.0 μM MC3181. All subtoxic concentrations of MC3181 (from 0.04 to 1.0 μM) were also able to efficiently reduce the h. N-cadherin expression up to 48 hours in WM266.4 cells (**P < 0.005 and ***P < 0.0005 vs control). Phosphorylated and non-phosphorylated proteins levels were quantitated by densitometry and normalized to their respective β-actin bands; data, presented as arbitrary units, represent means ± SD of three independent experiments. The x-axis is in logarithmic scale.
