FIGURE 1.
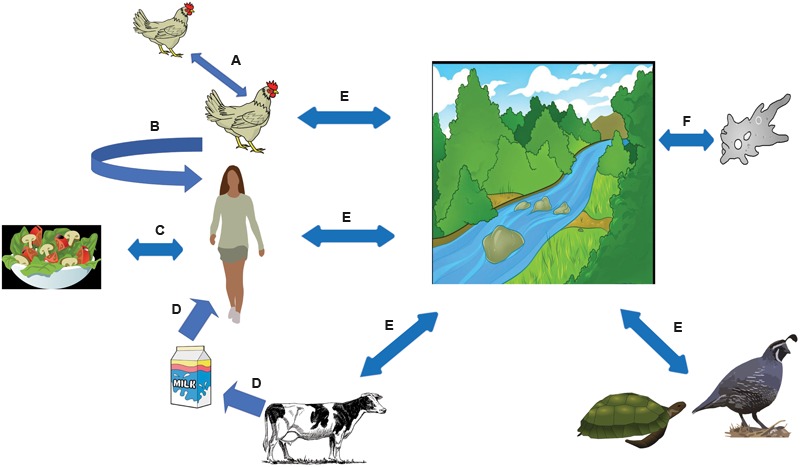
Campylobacter spp. modes of infection. Campylobacter spp. reside in large numbers in the gastrointestinal tract of chickens, where the bacteria is spread throughout the flock via the fecal-oral route (A) (Young et al., 2007). In the developed world, Campylobacter is usually acquired by consuming under-cooked poultry (B). However, outbreaks have been associated with different types of fresh produce (C) (Kärenlampi and Hänninen, 2004) and dairy products (D) (El-Zamkan and Hameed, 2016). Campylobacter spp. is frequently found in surface water, usually from contamination from animal feces, and has been known to infect humans (E) (Mughini-Gras et al., 2016). It has also been postulated that Campylobacter may be able to infect amoebae, which may serve as a reservoir (F) (Axelsson-Olsson et al., 2005).
