Fig. 3.
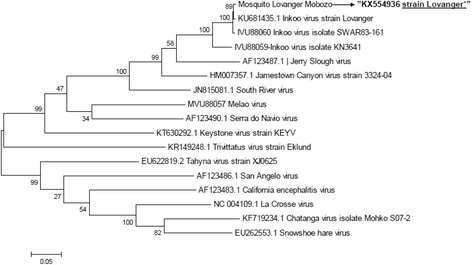
Phylogenetic analysis of the INKV M segment in comparison to 16 other viruses belonging to California serogroup. The M segment (KX554936) differed most from other INKV isolates, but most closely related to INKV Lövånger strain (KU681435), previously isolated from Ae. communis larvae in Västerbotten. The evolutionary history was inferred by using the Maximum Likelihood method based on the Tamura-Nei model [22]. There were a total of 4,612 positions in the final dataset. Evolutionary analyses were conducted in MEGA6 [21]. The study isolate is indicated in bold. Accession numbers; the study isolate INKV Lövånger strain (KX554936), Inkoo virus strain Lövånger (KU681435.1), Inkoo virus isolate SWAR83-161 (IVU88060), Inkoo virus KN 3641 (IVU88059), Jerry Slough virus (AF123487.1), James Canyon virus (HM007357.1), South River virus (JN815081), Melao virus (MVU88057), Serra do Navio virus (AF123490.1), Keystone virus strain KEYV (KT630292.1), Trivittatus strain Eklund (KR149248.1), Tahyna virus strain XJ0625 (EU622819.2), San Angelo virus (AF123486.1), Carlifornia encephalitis virus (AF123483.1), La rosse virus (NC004109.1), Chatanga virus isolate Mohko S07-2 (KF719234.1) and Snowshoe hare virus (EU262553.1) respectively
