Figure 4. Xenotransplanted adult bone marrow Lin-CD34+CD38lo hematopoietic stem cells give rise to human CD19+ B cells, including B-1 cells.
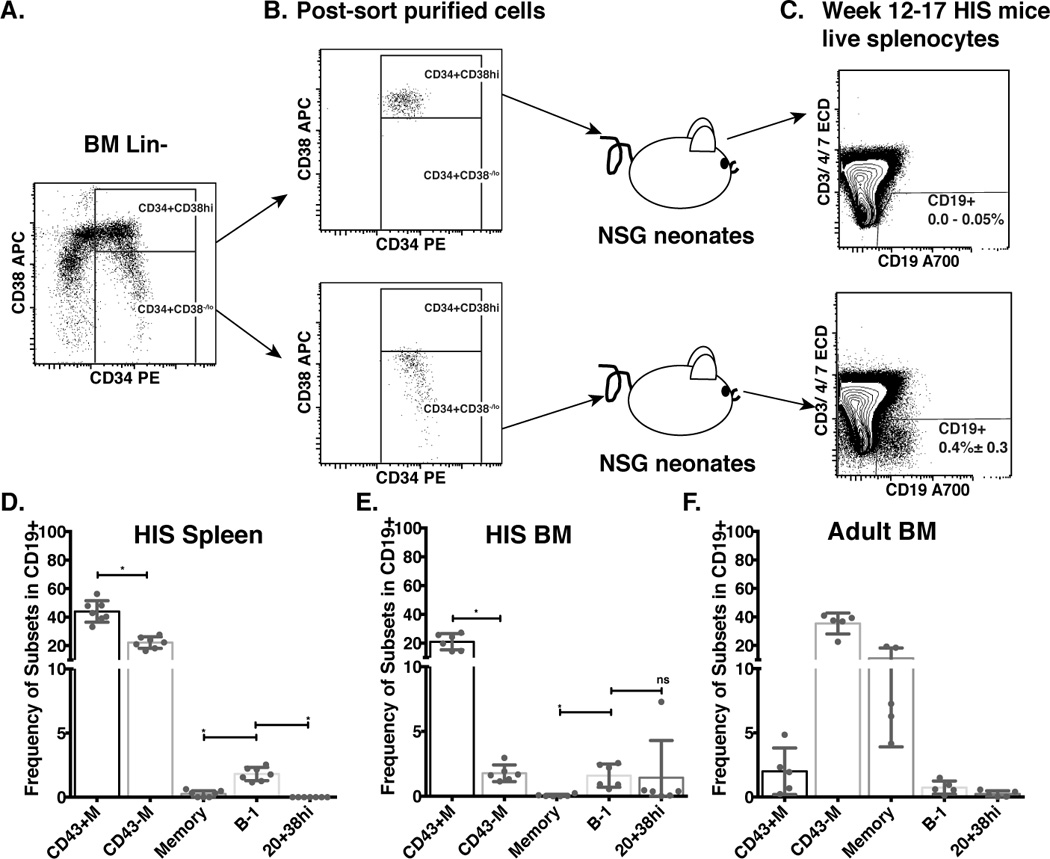
Lineage negative (Lin−) cells were isolated from bone marrow mononuclear cells and stained as described in Figure 1. A. Dot plot representation of CD34 versus CD38 expression of Lin− gated cells. B. Dot plots show purity of sort purified Lin−CD34+CD38hi (top panel) and Lin−CD34+CD38lo (lower panel) cells prior to transfer into NSG neonates to generate HIS mice. C. Dot plots show reconstituted human B (CD19+, CD3/4/7−) cells from spleens of HIS mice 12–17 weeks after transplant with sort purified human bone marrow CD34+CD38hi (top panel, number displays the range of events in the CD19+ gate), or Lin−CD34+CD38lo (lower panel, number displays the frequency means of events ± SD in the CD19+ gate) cells). D–E. Spleen (D) and Bone Marrow (BM, E) mononuclear cells from 12–17 week HIS mice were isolated and stained for B cell subset markers as in Figure 2A. Bar graphs show the frequencies of selected B cell subsets in individual mice (n=6) (nsp>0.05, *p≤0.05, Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank test). F. Bar graph shows the frequencies of selected B cell subsets in human adult bone marrow mononuclear cells (8 bone marrow samples were analyzed).
