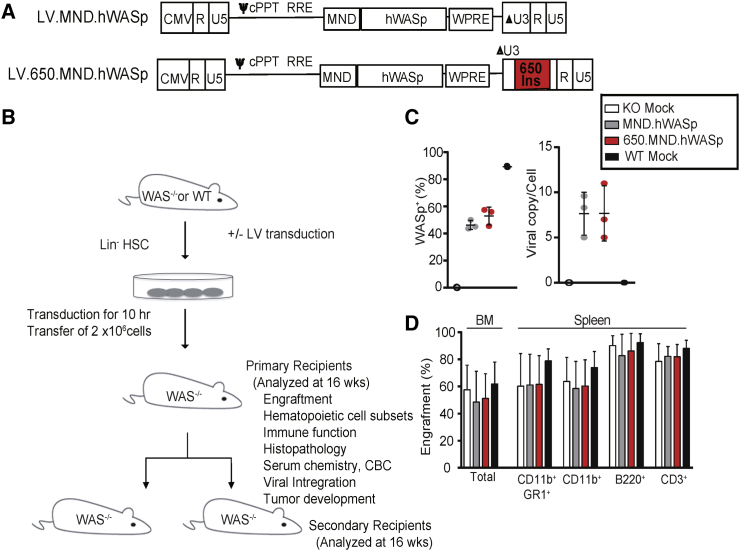
Figure 1.
Evaluation of a Clinical SIN-LV for the Treatment of WAS in a Mouse Gene Therapy Model
(A) Configuration of SIN-LVs used. Expression of hWASp (with a 3′ UTR consisting of the woodchuck hepatitis virus post-transcriptional regulatory element [WPRE]) is driven by an MND promoter. Both of the 5′ long terminal repeats (LTRs) are composed of the following: a cytomegalovirus (CMV) promoter and HIV-1 R and U5 regions; the 3′ LTR of both viruses have R and U5 regions and a modified U3 region (promoter deleted; ΔU3); the insulated version (below) has a 650-bp fragment derived from the cHS4 element inserted into the ΔU3 region of the LV LTR (650 INS; red box). cPPT, central polypurine track; ψ, Psi packaging sequence; RRE, Rev response element. (B) Experimental design for in vivo studies; further details are described in the Materials and Methods. (C) Percentage of gene therapy-treated Lin− cells expressing hWASp (left) and the lentiviral copy number (VCN) per cell (right) of an aliquot of input cells cultured for 7 days. (D) Percentage of donor cells (expressing donor CD45 allele) in total BM and splenic subsets 16 weeks after transplantation with gene therapy-treated Lin− BM. Means ± SD are shown.