Figure 1.
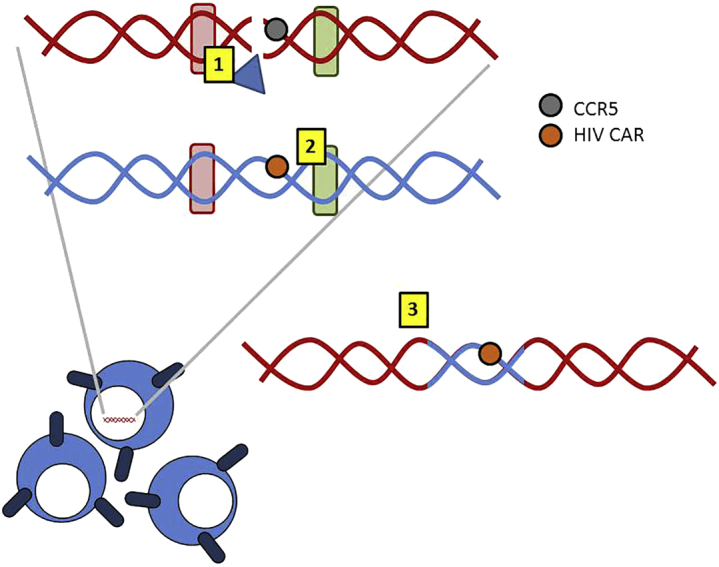
Harnessing Homology-Directed Repair for Gene Modification
Homology-directed repair (HDR), represented here, (1) employs double strand breaks introduced by the megaTAL (blue triangle) in the region of interest (i.e., CCR5) and initiates repair via the (2) homologous regions (rounded red and green rectangles) present in a donor template to (3) switch in a transgene of interest (i.e., the chimeric antigen receptor targeting HIV [HIV CAR]) during the repair process. The use of HDR to introduce constructs has the advantages of simultaneously removing a gene while introducing a new one and of directed integration (avoiding potentially “unsafe” regions).
