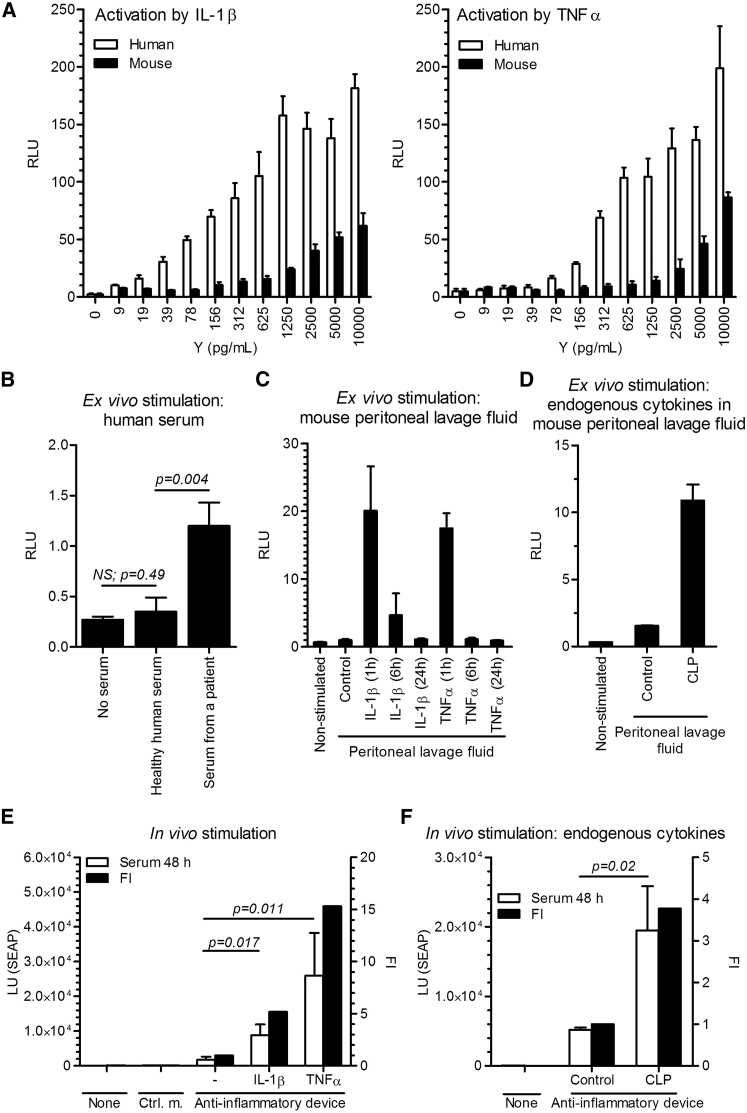
Figure 4.
Activation of the Anti-inflammatory Device In Vitro and In Vivo
(A) The responsiveness of the system to recombinant human and mouse interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) was tested in the anti-inflammatory device-engineered HEK293T cells by a dual luciferase test (reporter pAS51; TRE-UAS-PMIN-Luc) after a 24-hr activation period. Error bars indicate SD (n = 4). (B) The responsiveness of the system to pooled healthy human serum (n = 4) and the serum of a patient with systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis (sJIA). Error bars indicate SD (n = 4). (C) Activation of the anti-inflammatory device-engineered HEK293T cells ex vivo by a peritoneal lavage fluid of mice, injected i.p. with hIL-1β (300 ng/mice) or hTNF-α (250 ng/mice). The peritoneal lavage fluid was collected at different time points. Error bars indicate SD (n = 4). (D) Activation of the anti-inflammatory device-engineered HEK293T cells ex vivo by endogenous mouse cytokines in a peritoneal lavage fluid of mice that were subjected to the cecal ligation and puncture (CLP). The peritoneal lavage fluid was collected 24 hr after CLP procedure. Error bars indicate SD (n = 4). (E) The responsiveness of the system in vivo. The anti-inflammatory device-engineered HEK293T cells (reporter pAS72; TRE-UAS-PMIN-SEAP) were microencapsulated and implanted i.p. An inflammatory signal was induced i.p. with an injection of hIL-1β (300 ng/mouse) or hTNF-α (250 ng/mouse) 1 and 24 hr post-implantation. Serum SEAP levels were profiled after 48 hr. Error bars indicate SD (n = 5). (F) The responsiveness of the implanted anti-inflammatory device to endogenous CLP-induced inflammation in mice. CLP procedure was performed 24 hr before microcapsules implantation, and SEAP levels were measured 48 hr post-implantation. Y, mass concentration; FI, fold induction; Ctrl. m., control microcapsules; Control, control mice. Error bars indicate SD (n = 5).