Figure 6.
Reversibility of the Synthetic Anti-inflammatory Device In Vitro and In Vivo
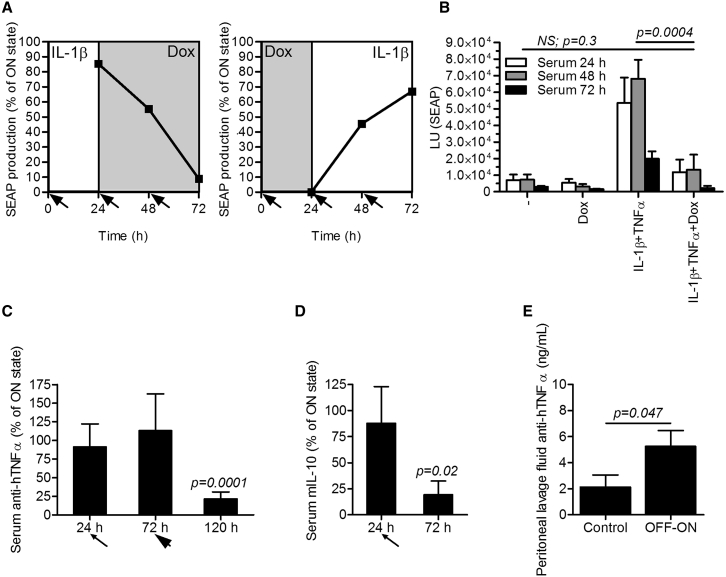
(A) Reversibility of the synthetic anti-inflammatory device in vitro. Left: shutdown of the system. The anti-inflammatory device-engineered HEK293T cells (reporter pAS72; TRE-UAS-PMIN-SEAP) were stimulated with hIL-1β (1 ng/mL) for 24 hr and then shut down by the addition of the doxycycline (Dox) (1 μg/mL) by exchanging the medium (indicated by the arrows). Right: rebooting of the initially shut down system. The anti-inflammatory device-engineered HEK293T cells (reporter pAS72; TRE-UAS-PMIN-SEAP) were shut down by Dox (1 μg/mL) for 24 hr and then reactivated by the addition of hIL-1β (1 ng/ml) during medium exchange (indicated by the arrows). Error bars indicate SD (n = 4). (B) In vivo restraint of the full system activation. The anti-inflammatory device-engineered HEK293T cells (reporter pAS72; TRE-UAS-PMIN-SEAP) were microencapsulated and implanted i.p. One hour after implantation, the mice were injected i.p. with a combination of 300 ng of hIL-1β and 250 ng of hTNF-α per mouse. After 1 hr and then every 24 hr, the device was shut down by an i.v. Dox injection (20 mg/kg). Serum was collected daily, and SEAP levels were measured. (C and D) In vivo shut down of the system. The anti-inflammatory device-engineered HEK293T cells (effector pAS134; TRE-UAS-PMIN-anti-hTNF-α Ab-mIL-10) were microencapsulated, implanted i.p., and fully activated by injection of a combination of 300 ng of hIL-1β and 250 ng of hTNF-α per mouse. After 24 hr (thin arrow), the device was shut down by an i.v. Dox injection (20 mg/kg). (C) The device was additionally activated and shut down after 72 hr (thick arrow) to reach the relevant time span needed for an observation of the anti-hTNF-α antibody kinetics. Serum was collected at different time points, and (C) anti-hTNF-α antibody or (D) mIL-10 levels were measured. (E) Reactivation of the anti-inflammatory device in vivo. The anti-inflammatory device-engineered HEK293T cells (effector pAS134; TRE-UAS-PMIN-anti-hTNF-α Ab-mIL-10) were microencapsulated and shut down by i.v. Dox injection (20 mg/kg) 1 hr after implantation. After 72 hr, the system was activated by a single application of 300 ng of hIL-1β and 250 ng of hTNF-α per mouse. Implanted anti-inflammatory device alone represented the control group. Anti-hTNF-α antibody concentration was profiled in the peritoneal lavage fluid 120 hr after implantation. Error bars indicate SD (n = 4).