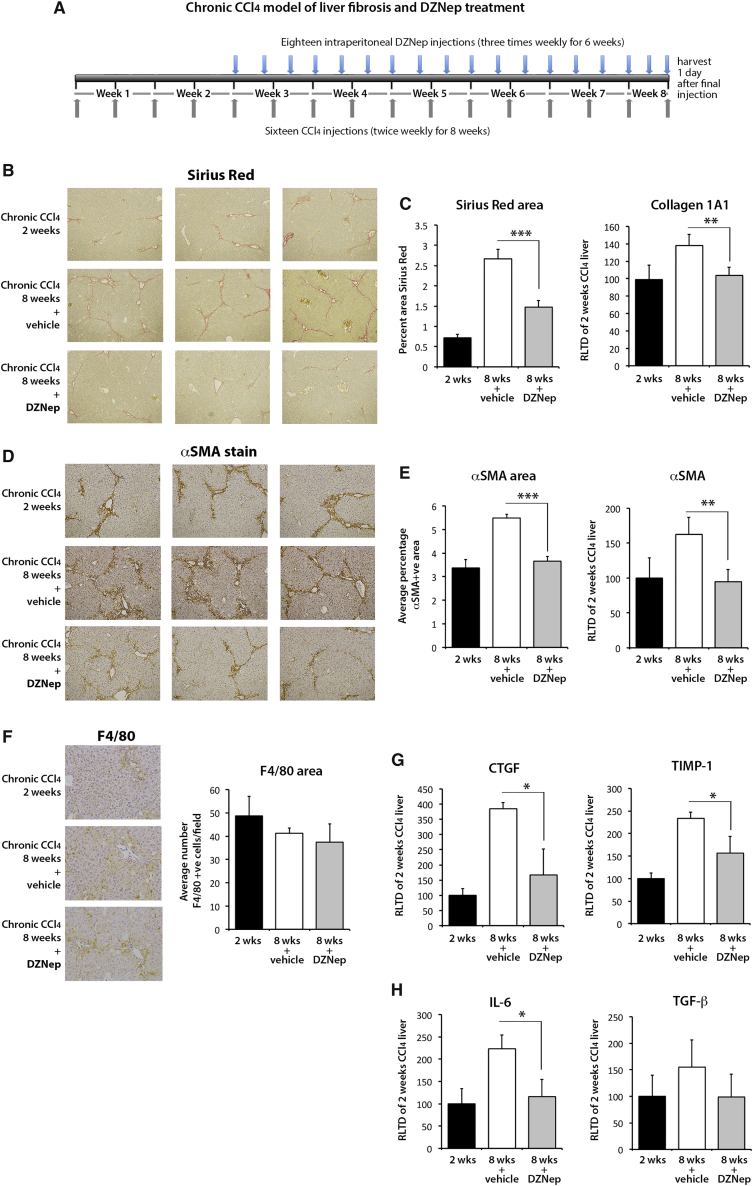
Figure 2.
DZNep Prevents Fibrosis Progression in a Chronic Model of CCl4-Induced Liver Fibrosis
(A) Schematic representation of chronic CCl4 model of liver fibrosis combined with progressive therapeutic treatment with DZNep. Grey arrows show frequency of CCl4 injections, whereas blue arrows show DZNep injections. Briefly, liver fibrosis was established for 2 weeks followed by administration of DZNep treatment alongside CCl4 for a further 6 weeks. (B) Histological sections showing collagen staining (Sirius Red). (C) Graphs showing average percentage area for Sirius Red (left) and mRNA levels of Collagen 1A1 as quantified by qPCR in livers from all animals in the study (right). (D) αSMA staining in three representative control or DZNep-treated animals as well as the animals at the starting point of treatment (2 weeks CCl4). (E) Graphs showing average percentage area αSMA in all groups (left) and mRNA levels of αSMA as quantified by qPCR in livers (right). (F) Histological sections showing macrophage staining (F4/80, left panels) and graphs showing average number of F4/80 positive cells per field (right panel). (G) mRNA levels for XTΓΦ, TΙΜΠ−1, (H) ΙΛ−6, and TΓΦβ1 as quantified by qPCR in livers of all animals. Error bars in relevant panels represent mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001.