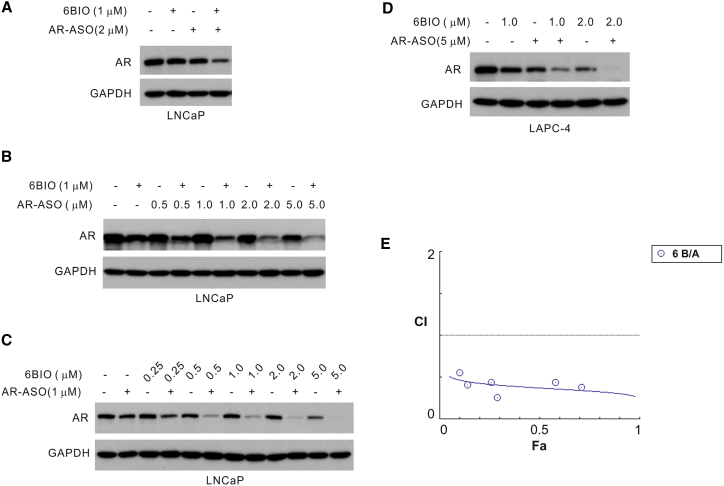
Figure 5.
Titration Experiments Using the AR-ASO and 6BIO Demonstrate a Reduced AR Expression in Prostate Cancer Cells
Western analyses of lysates harvested from LNCaP (A–C) or LAPC-4 cells (D). (A) LNCaP cells treated with (+) or without (−) 1 μM 6BIO or 2 μM AR-ASO. The combined treatment of 6BIO and the AR-ASO reduced AR protein expression by approximately 70%. Either 6BIO or AR-ASO alone reduced the AR protein expression by only approximately 25%. Values of protein reduction were calculated with ImageJ and normalized to the GAPDH as the loading control and to the control, untreated cells. (B) LNCaP cells treated with 1 μM 6BIO with (+) or without (−) the indicated concentrations of AR-ASO. (C) LNCaP cells treated with 1 μM AR-ASO with (+) or without (−) the indicated concentrations of 6BIO. (D) LAPC-4 cells with 5 μM AR-ASO with (+) or without (−) the indicated concentrations of 6BIO. In all experiments, the AR-ASO was delivered by gymnosis for 2 days. Experiments were repeated a minimum of two times with consistent results. (E) Combination index (CI) plot calculated with the CI equation algorithms using CompuSyn software.35 The values were derived from the quantitation of AR protein suppression by the combined use of 6BIO and AR-ASO (Figure S2). CI = 1 indicates an additive effect of the drugs; CI > 1 indicates an antagonistic effect; CI < 1 demonstrates synergism.