Figure 2. c-Myc suppresses expression of miR-451 via recruiting HDAC3.
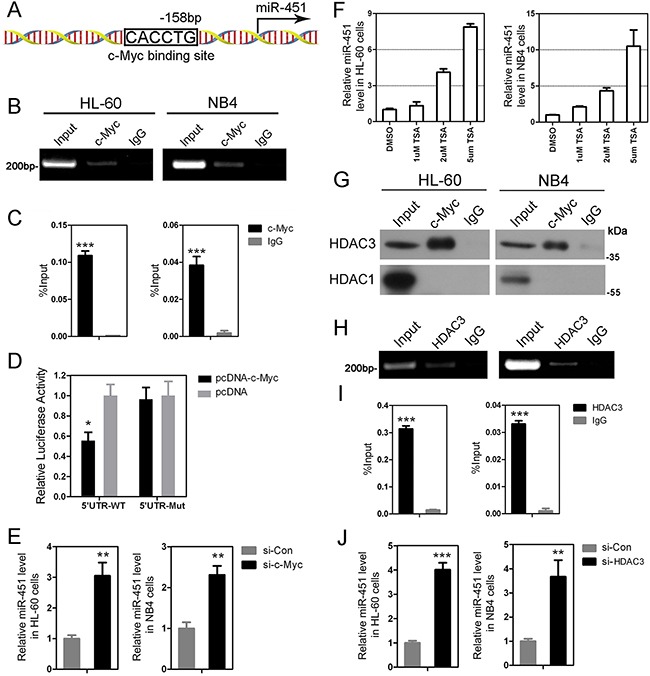
A. A sketch showing the c-Myc binding site at −158 bp upstream of the miR-451 promoter. The other potential binding sites, which are not been confirmed by ChIP-PCR, are not shown. B. The ChIP-PCR data indicate that c-Myc binds on the c-Myc binding site at −158 bp upstream of the miR-451 promoter in HL-60 and NB4 cells. C. Quantitative ChIP-PCR demonstrates a significant enrichment of c-Myc on the promoter region of miR-451 in the AML cells. D. Enforced expression of c-Myc by pcDNA-c-Myc tensfection inhibits the activity of miR-451 promoter. The dual-luciferase reporter assay was performed in triplicate in HEK-293 cells. Error bars represent SD. * P<0.05; Student's t-test. E. Knowdown of c-Myc by si-c-Myc transfection increased miR-451 level in HL-60 and NB4 cells. **P<0.01. F. TSA treatment significantly induces expression of miR-451 in the AML cells at a dose-dependent manner. G. The Co-IP assay indicates that c-Myc can interact with HDAC3, but not HDAC1, in Hl-60 and NB4 cells. H. ChIP-PCR shows HDAC3 binds on the same location of miR-451 promoter with c-Myc. I. Quantitative ChIP-PCR analysis demonstrated a significant enrichment of HDAC3 on the promoter region of miR-451 in the AML cells. ***P<0.001. J. Inhibition of HDAC3 by si-HDAC3 transfection dramatically accelerates expression of miR-451 in the AML cells. **P<0.01; ***P<0.001.
