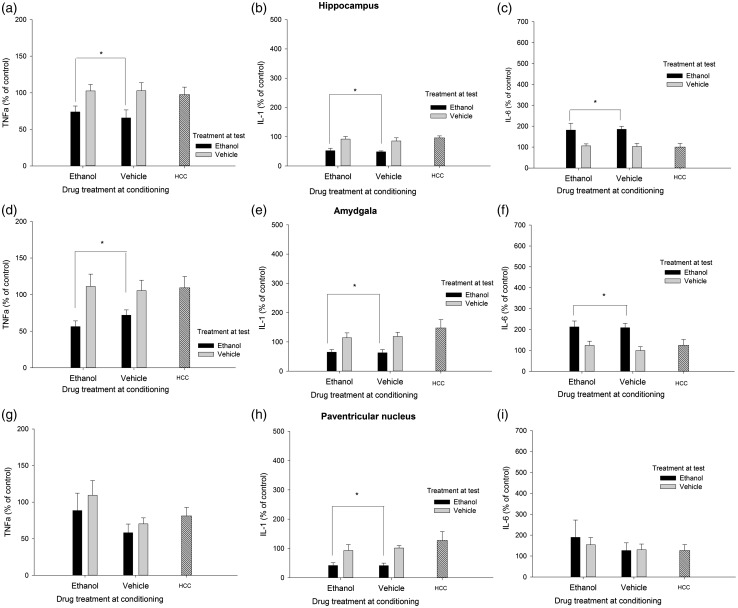
Figure 4.
Cytokine expression (mRNA levels of tumor necrosis factor alpha [TNFα], Interleukin-1β [IL-1], and interleukin-6 [IL-6], obtained via RT-PCR) in the hippocampus, amygdala, and paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus of male Sprague Dawley rats that, during conditioning, were given two administrations of lemon-flavored ethanol (4.0 g/kg, intragastrically) or vehicle (tap water flavored with a non-alcoholic lemon extract [1%]). At test, the rats were sacrificed 3 h after an intubation with lemon-flavored water or 4.0 g/kg ethanol (flavored with lemon). An additional home cage control (HCC) group received no manipulation and remained in home cage for the duration of the experiment. All data are normalized to glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH), and expressed relative to the HCC control group . The asterisks in Panels A, B, D, E, and H indicate that ethanol treatment at test significantly reduced TNFα or IL-1β levels, when compared to the levels of these transcript found in vehicle-treated or HCC animals (p < 0.05). The asterisks in Panels C and F indicate that ethanol treatment at test significantly enhanced IL-6 levels, when compared to the levels observed in vehicle-treated or HCC animals (p < 0.05). The error bar indicates SEM