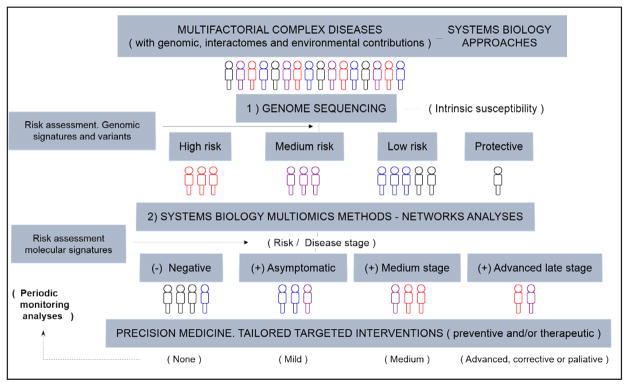
Figure 1.
The systems biology (SB) paradigm for complex multifactorial diseases: from SB-based approaches to precision medicine. Pipeline. Multifactorial diseases involve genomics, interactomes, and environmental contributions for which SB-based approaches are needed. Comprehensive screenings of individuals, groups, and subgroups need to start with advanced genome sequencing methods in order to unveil specific variants and genomic signatures for basic risk assessment at genomic level (i.e. intrinsic susceptibility to disease) (point 1). From here, further comprehensive systems-level analyses, with SB multi-omics networks methods, both experimental and computational, are needed (point 2) (14–16). These advanced methods, with incorporation of new standardized techniques and guidelines, are expected to reveal specific molecular signatures and biomarker patterns in time and space, underlying mechanisms and actual disease risk and disease stage, towards mechanistically-based, rational-tailored interventions, preventive and/or therapeutic (i.e. “true precision medicine” paradigm) (14–15)