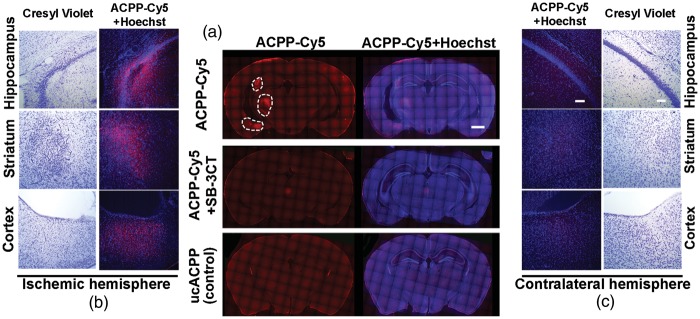
Figure 3.
Association of ACPP-Cy5 uptake with neuronal cell death seven days after embolic MCA occlusion in mice. ACPP-Cy5 or uncleavable ACPP-Cy5 (2 nmol) was injected i.v. seven days after embolus-induced MCA occlusion and 4 h prior to sacrifice of the mice. (a) Deconvolution microscopy reveals ACCP-Cy5 (red) uptake in ischemic region. Gelatinase selective inhibitor SB-3CT (25 mg/kg) attenuated the uptake of ACPP-Cy5 in ischemic regions. The cleavage-resistant ACPP (ucACPP) control was not detectable in the ischemic regions. (b) Neuronal cell death in the ischemic region was confirmed by cresyl violet staining, which revealed irregular, condensed cell bodies compared to round, faintly-stained healthy neurons in the contralateral region. ACPP-Cy5 uptake into the ischemic hemisphere correlated with neuronal cell death identified by cresyl violet staining in cortex, striatum, and hippocampus. (c) Corresponding regions of the contralateral hemisphere are shown for comparison. Scale bar, 1 mm (a) and 100 µm (b and c).