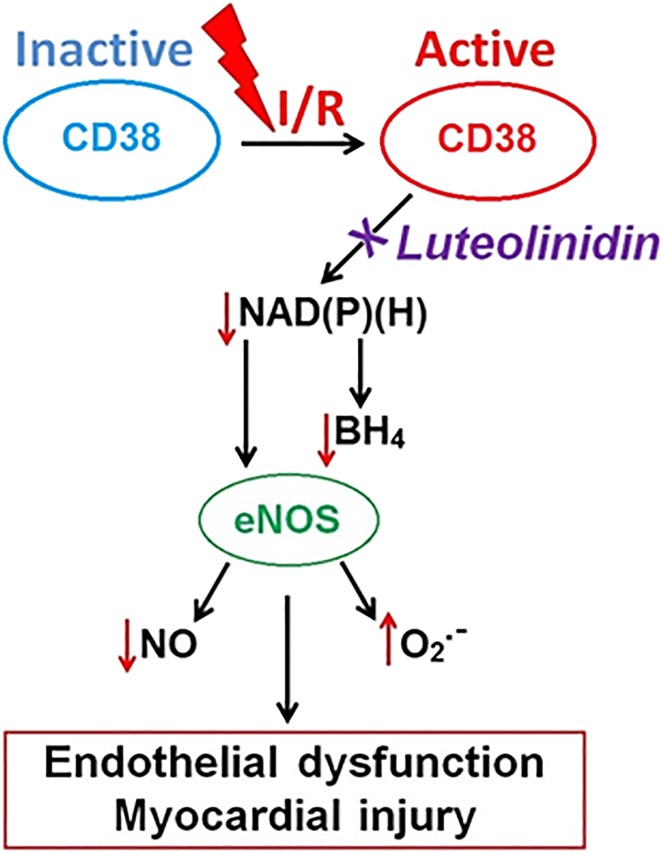
Fig. 1.
Schematic depicting role of CD38 activation with I/R injury. After I/R, depletion of the NAD(P)(H) pools occurs by enzymatic degradation of NAD(P)+ by the NAD(P)+ase CD38. Low NADPH levels in turn contribute to low BH4 levels due to the presence of NADPH-dependent enzymes in both the de novo synthesis and recycling pathways for BH4. Together, low NADPH and BH4 levels contribute to eNOS uncoupling where production of NO is lost and generation of superoxide (O2.-) occurs, leading to endothelial dysfunction and myocardial injury.