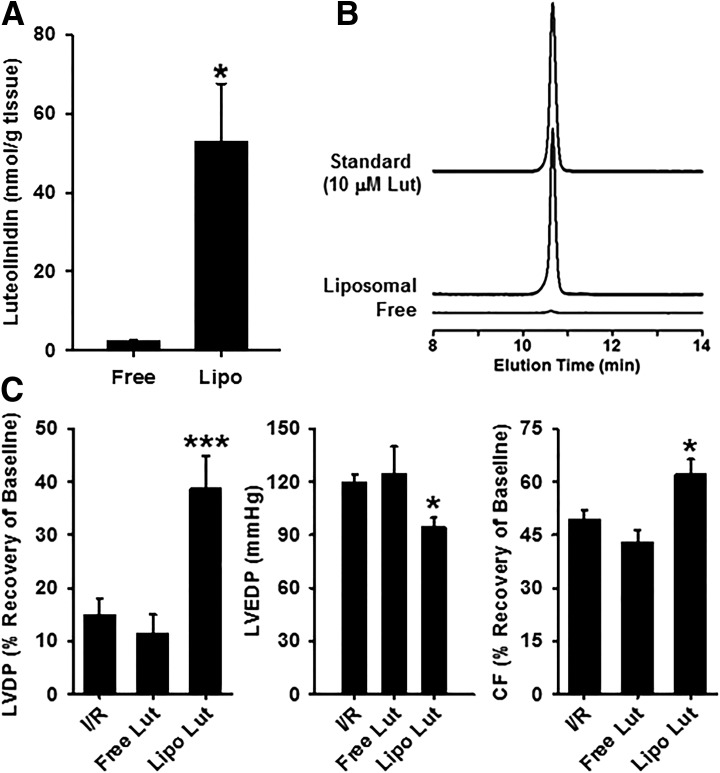
Fig. 4.
Tissue uptake of luteolinidin and postischemic protection. (A) The levels of luteolinidin in heart tissue after 25 μM luteolinidin delivery in KHB (aqueous) or liposomal solution. Although aqueous delivery of luteolinidin failed to efficiently raise tissue luteolinidin concentration, liposomal delivery was highly effective. *P < 0.05 (mean ± S.E.M., n = 3). (B) Chromatograms showing the elution profile of luteolinidin from homogenates of hearts receiving aqueous and liposomal luteolinidin (25 μM) and from a 10 μM standard of luteolinidin. (C) Functional recovery in untreated hearts subjected to I/R (I/R), hearts treated with 25 μM luteolinidin in Krebs buffer (Free Lut), and hearts treated with 25 μM liposomal luteolinidin (Lipo Lut). Luteolinidin delivered in Krebs buffer (Free Lut) had no effect on the recovery of LVDP, LVEDP, or CF after I/R, whereas liposomal luteolinidin provided significant protection. *P < 0.05; ***P < 0.005 (Lipo Lut versus I/R or Free Lut versus I/R; mean ± S.E.M., n = 3–10).