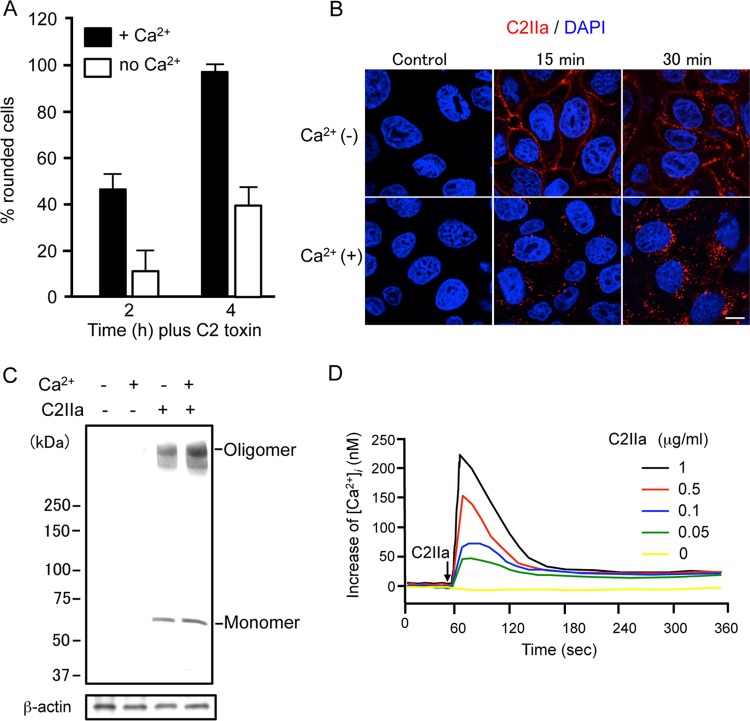
FIG 1.
Effect of Ca2+ on the action of C2 toxin. (A) MDCK cells were incubated in either Ca2+ (1.8 mM) medium or Ca2+-free medium with C2I (100 ng/ml) and C2IIa (200 ng/ml) at 37°C for the periods indicated. Pictures were taken. About 100 cells were counted per picture, and the number of rounded cells was determined as a percentage. Values are given as means ± standard deviations (n = 3). (B) MDCK cells were incubated with C2IIa (1 μg/ml) at 37°C for the periods indicated. Cells were fixed, permeabilized, and stained with an anti-C2IIa antibody and DAPI. C2IIa (red) and the nucleus (blue) were viewed by using a confocal microscope. The experiments were repeated three times, and a representative result is shown. Bar, 7.5 μm. (C) MDCK cells were incubated in either Ca2+ (1.8 mM) medium or Ca2+-free medium with C2IIa (1 μg/ml) at 37°C for 30 min. The cells were rinsed and subjected to Western blot analyses of C2IIa and β-actin (control). A typical result from one of three experiments is shown. (D) MDCK cells were loaded with the intracellular Ca2+ indicator Fura-2/AM. [Ca2+]i was calculated as described in Materials and Methods. Changes in [Ca2+]i induced by C2IIa were measured in cells in extracellular buffer containing 1.8 mM CaCl2. C2IIa was added at the time indicated by the arrow. A typical result from three independent experiments is shown.