FIG 4.
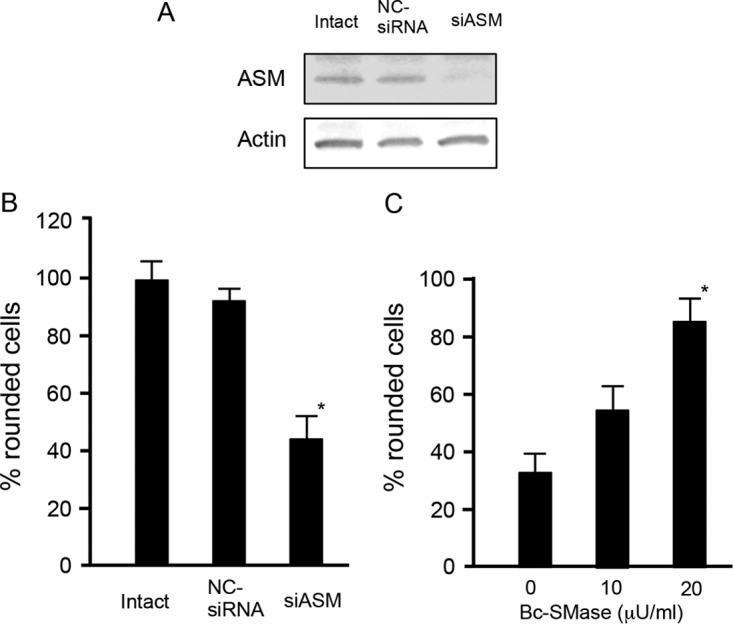
Role of acid sphingomyelinase in C2 toxin-induced cytotoxic effects on Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. siRNAs were used to reduce cellular ASMase levels (siASM) with a nonsilencing siRNA used as a control (NC-siRNA). (A) Western blots were used to determine the reduction in ASMase levels. A typical result from one of three experiments is shown. (B) After siRNA treatment, cells were incubated with C2I (200 ng/ml) and C2IIa (500 ng/ml) at 37°C for 4 h. About 100 cells were counted per picture, and the number of rounded cells was determined as a percentage. Values are given as means ± standard deviations (n = 4). Two-tailed Student's t test was employed to assess statistical significance. *, P < 0.01 (significantly different from NC-siRNA-treated cells plus C2 toxin). (C) MDCK cells were treated with or without 10 or 20 μU/ml of sphingomyelinase (SMase) from Bacillus cereus for 30 min and then rinsed. Cells were incubated with C2I (100 ng/ml) and C2IIa (200 ng/ml) at 37°C for 4 h. About 100 cells were counted per picture, and the number of rounded cells was determined as a percentage. Values are given as means ± standard deviations (n = 3). Two-tailed Student's t test was employed to assess statistical significance. *, P < 0.01 (significantly different from Bc-SMase-untreated cells plus C2 toxin).
