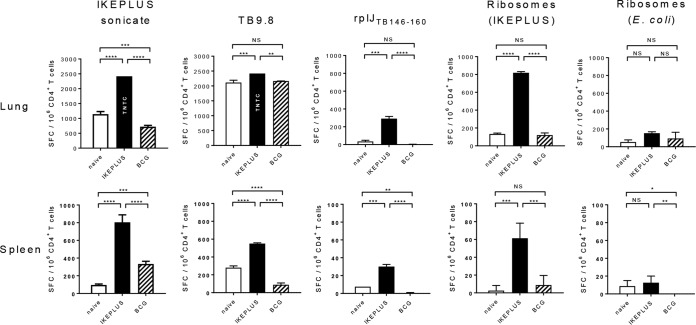
FIG 7.
Ribosome-specific CD4+ T cell responses following M. tuberculosis challenge. Mice (C57BL/6) were immunized with 5 × 107 CFU IKEPLUS i.v. or 107 CFU BCG-Danish s.c. or sham immunized with saline s.c. (naive). Ten weeks later, immunized and naive mice were challenged with a low-dose aerosol delivery of M. tuberculosis strain H37Rv (∼100 CFU). Six weeks after challenge, CD4+ T cells were purified from spleens and lungs and tested by an ELISPOT assay for the production of IFN-γ in response to ex vivo stimulation with the indicated antigens (the IKEPLUS sonicate [10 μg/ml], the TB9.8 peptide [10 μg/ml], the rplJTB146–160 peptide [10 μg/ml], the ribosome-enriched fraction from IKEPLUS [5 nM], or purified E. coli ribosomes [5 nM]). Bars show mean numbers of IFN-γ spot-forming cells (SFC) in response to the indicated antigens for groups of 4 mice, with background values (mean number of IFN-γ spot-forming cells per 106 CD4+ T cells in response to culture medium alone) being subtracted, and error bars indicate 1 standard deviation. Background values (mean ± 1 standard deviation) were as follows: 8 ± 9 spot-forming cells for naive spleen, 11 ± 9 spot-forming cells for IKEPLUS spleen, 36 ± 9 spot-forming cells for BCG spleen, 120 ± 6 spot-forming cells for naive lung, 84 ± 19 spot-forming cells for IKEPLUS lung, and 68 ± 25 spot-forming cells for BCG lung. Responses that were significantly different between IKEPLUS-immunized, BCG-immunized, and unimmunized animals are indicated. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001 (as determined by ANOVA). TNTC, too numerous to count (estimated to be 2,500 spot-forming cells).